
들어가며
안녕하세요! Devlos입니다.
이번 포스팅은 CloudNet@ 커뮤니티에서 주최하는 Cilium Study 6주 차 주제인 "Cilium Service Mesh"에 대해서 정리한 내용입니다.
실습환경 구성
이번 주차 실습 환경은 mac M3 Pro max 환경에서 실습을 진행했고, VirtualBox + Vagrant로 환경을 구성했어요.
실습환경은 다음과 같습니다
버전
- k8s(1.33.4), cilium(1.18.1), pwru
- 가상 머신 구성
- k8s-ctr-spec: vCPU 4, Memory 2560
- k8s-w-spec: vCPU 4, Memory 2560
(해당 스펙보다 성능이 낮으면 VM이 꺼질 수 있어요. 자원을 많이 씁니다.)
실습환경 구성
지난주 세팅과 크게 다르지 않아, 설명은 생략하겠습니다.
mkdir cilium-lab && cd cilium-lab
curl -O https://raw.githubusercontent.com/gasida/vagrant-lab/refs/heads/main/cilium-study/6w/Vagrantfile
vagrant up
실습 환경 정상 설정 확인
샘플 서비스를 배포해 보고, 통신이 잘 동작하는지 확인합니다.
# 샘플 애플리케이션 배포
cat << EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: webpod
spec:
replicas: 2
selector:
matchLabels:
app: webpod
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: webpod
spec:
affinity:
podAntiAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
- labelSelector:
matchExpressions:
- key: app
operator: In
values:
- sample-app
topologyKey: "kubernetes.io/hostname"
containers:
- name: webpod
image: traefik/whoami
ports:
- containerPort: 80
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: webpod
labels:
app: webpod
spec:
selector:
app: webpod
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 80
targetPort: 80
type: ClusterIP
EOF
# k8s-ctr 노드에 curl-pod 파드 배포
cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: curl-pod
labels:
app: curl
spec:
nodeName: k8s-ctr
containers:
- name: curl
image: nicolaka/netshoot
command: ["tail"]
args: ["-f", "/dev/null"]
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 0
EOF
# 배포 확인
kubectl get deploy,svc,ep webpod -owide
kubectl get endpointslices -l app=webpod
kubectl get ciliumendpoints # IP 확인
# 통신 문제 확인
kubectl exec -it curl-pod -- curl -s --connect-timeout 1 webpod | grep Hostname
kubectl exec -it curl-pod -- sh -c 'while true; do curl -s --connect-timeout 1 webpod | grep Hostname; echo "---" ; sleep 1; done'
# cilium-dbg, map
kubectl exec -n kube-system ds/cilium -- cilium-dbg ip list
kubectl exec -n kube-system ds/cilium -- cilium-dbg endpoint list
kubectl exec -n kube-system ds/cilium -- cilium-dbg service list
kubectl exec -n kube-system ds/cilium -- cilium-dbg bpf lb list
kubectl exec -n kube-system ds/cilium -- cilium-dbg bpf nat list
kubectl exec -n kube-system ds/cilium -- cilium-dbg map list | grep -v '0 0'
kubectl exec -n kube-system ds/cilium -- cilium-dbg map get cilium_lb4_services_v2
kubectl exec -n kube-system ds/cilium -- cilium-dbg map get cilium_lb4_backends_v3
kubectl exec -n kube-system ds/cilium -- cilium-dbg map get cilium_lb4_reverse_nat
kubectl exec -n kube-system ds/cilium -- cilium-dbg map get cilium_ipcache_v2✅ 실행 결과 요약
디플로이먼트, 서비스, endpointslice, ciliumendpoints 등이 정상적으로 동작하는지 확인한 후, 통신테스트를 수행합니다.
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# kubectl get deploy,svc,ep webpod -owide
Warning: v1 Endpoints is deprecated in v1.33+; use discovery.k8s.io/v1 EndpointSlice
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE CONTAINERS IMAGES SELECTOR
deployment.apps/webpod 2/2 2 2 58s webpod traefik/whoami app=webpod
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE SELECTOR
service/webpod ClusterIP 10.96.134.235 <none> 80/TCP 58s app=webpod
NAME ENDPOINTS AGE
endpoints/webpod 172.20.0.128:80,172.20.1.140:80 58s
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# kubectl get endpointslices -l app=webpod
NAME ADDRESSTYPE PORTS ENDPOINTS AGE
webpod-nt4q6 IPv4 80 172.20.0.128,172.20.1.140 63s
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# kubectl get ciliumendpoints
NAME SECURITY IDENTITY ENDPOINT STATE IPV4 IPV6
curl-pod 29584 ready 172.20.0.2
webpod-697b545f57-f9dpx 32246 ready 172.20.1.140
webpod-697b545f57-wwjxp 32246 ready 172.20.0.128
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# kubectl exec -it curl-pod -- curl -s --connect-timeout 1 webpod | grep Hostname
Hostname: webpod-697b545f57-wwjxp
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# kubectl exec -it curl-pod -- sh -c 'while true; do curl -s --connect-timeout 1 webpod | grep Hostname; echo "---" ; sleep 1; done'
Hostname: webpod-697b545f57-f9dpx
---
Hostname: webpod-697b545f57-wwjxp
---
Hostname: webpod-697b545f57-wwjxp
---
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# kubectl exec -n kube-system ds/cilium -- cilium-dbg ip list
IP IDENTITY SOURCE
0.0.0.0/0 reserved:world
172.20.1.0/24 reserved:world
10.0.2.15/32 reserved:host
reserved:kube-apiserver Service Mesh란?
서비스 메시는 애플리케이션 네트워킹과 같은 공통적인 관심사를 애플리케이션 내부가 아니라 외부에서 투명하게 처리해주는 인프라를 의미합니다.
클라우드 환경에서 마이크로서비스를 운영할 때는 신뢰할 수 없는 네트워크, 서비스의 가용성, 복잡한 트래픽 흐름, 트래픽 암호화, 애플리케이션 상태 관리, 성능 등 다양한 도전과제들이 존재합니다. 이러한 문제들은 각 애플리케이션 내부에서 라이브러리를 활용해 서비스 디스커버리와 같은 패턴을 구현함으로써 어느 정도 해결할 수 있습니다.
또한 서비스의 관찰 가능성을 높이기 위해 메트릭이나 트레이싱을 생성하고 배포하려면 추가적인 라이브러리나 서비스가 필요합니다.
서비스 메시는 이런 공통적인 네트워킹 문제들을 애플리케이션 외부, 즉 프로세스 외부에서 투명하게 처리해주는 인프라라고 할 수 있습니다.
예를 들어, 이스티오(Istio)는 대표적인 서비스 메시 구현체로, 데이터 플레인과 컨트롤 플레인이라는 두 가지 주요 요소로 구성되어 있습니다. 데이터 플레인은 애플리케이션과 함께 배포되는 서비스 프록시로, 정책을 적용하고 트래픽을 제어하며, 메트릭과 트레이싱을 생성하는 등 애플리케이션을 보완하는 역할을 합니다. 컨트롤 플레인은 운영자가 데이터 플레인의 네트워크 동작을 제어할 수 있도록 API를 제공합니다.
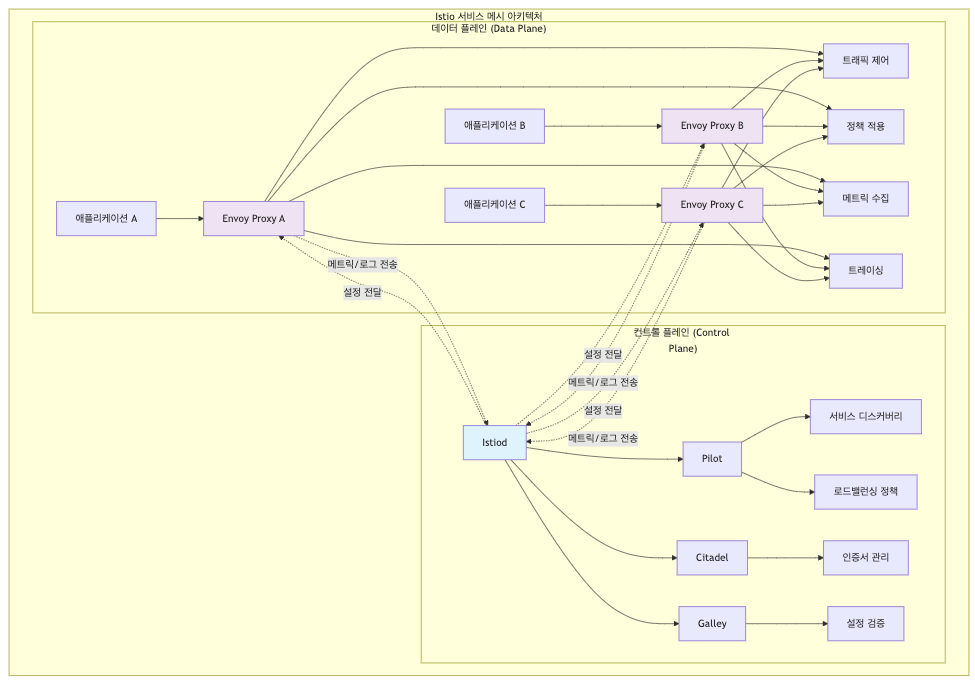
일반적으로 Service Mesh 구현을 위해 사용하는 이스티오에서는 엔보이(Envoy)를 서비스 프록시로 사용합니다. 엔보이는 다양한 기능을 제공하고, 동적으로 설정할 수 있기 때문에 서비스 메시 환경에서 널리 활용되고 있습니다.
Service Mesh를 사용하면 다음과 같은 이점을 누릴 수 있습니다.
트래픽 모니터링
- 서비스 메시를 도입함으로써 각 서비스 간의 트래픽에 대해 에러율, 레이턴시(지연 시간), 커넥션 개수, 요청 개수 등 다양한 메트릭을 실시간으로 수집하고 모니터링 가능
- 이러한 메트릭을 기반으로 특정 서비스 간의 통신이나 특정 요청 경로에 대해 필터링하여 분석함으로써 장애나 성능 저하의 원인을 보다 쉽게 파악할 수 있음
트래픽 컨트롤
- 서비스 메시를 통해 트래픽을 세밀하게 제어할 수 있음
- 트래픽 시프팅(Traffic shifting) 기능을 활용함으로써 전체 트래픽 중 99%는 기존 애플리케이션으로, 1%는 신규 애플리케이션으로 전달하는 식의 점진적 배포(카나리 배포)를 구현 가능
또한, 특정 단말이나 사용자를 신규 애플리케이션으로 유도함으로써 단계적으로 새로운 기능을 적용할 수 있음 - 서킷 브레이커(Circuit Breaker) 기능을 사용함으로써, 만약 목적지 마이크로서비스에 장애가 발생할 경우 해당 서비스로의 접속을 자동으로 차단하여 전체 시스템 장애를 예방할 수 있음
- 폴트 인젝션(Fault Injection) 기능을 통해서는 의도적으로 요청을 지연시키거나 실패하게 만들어 장애 상황을 시뮬레이션하고, 시스템의 복원력이나 장애 대응 능력을 사전에 검증할 수 있음
- 속도 제한(Rate Limit) 기능을 활용함으로써 특정 서비스에 대한 요청 개수를 제한하여 과도한 트래픽으로 인한 서비스 장애를 방지
Istio Service Mesh에 대한 세부사항은 이전 스터디 내용에서 확인 가능합니다. 링크- https://devlos.tistory.com/100
Istio Service Mesh VS Cilium Service Mesh
Cilium은 CNI(컨테이너 네트워크 인터페이스)이면서 동시에 Service Mesh 기능까지 제공하는 독특한 솔루션입니다.
아래 그림은 전통적인 Service Mesh(Sidecar 방식, 좌측)와 Cilium(eBPF 기반, 우측) Service Mesh 구조를 비교한 것입니다. Cilium은 eBPF를 통해 커널 레벨에서 네트워크 트래픽을 처리함으로써, 별도의 프록시 없이도 서비스 메시의 주요 기능을 제공할 수 있다는 점이 큰 차이입니다.
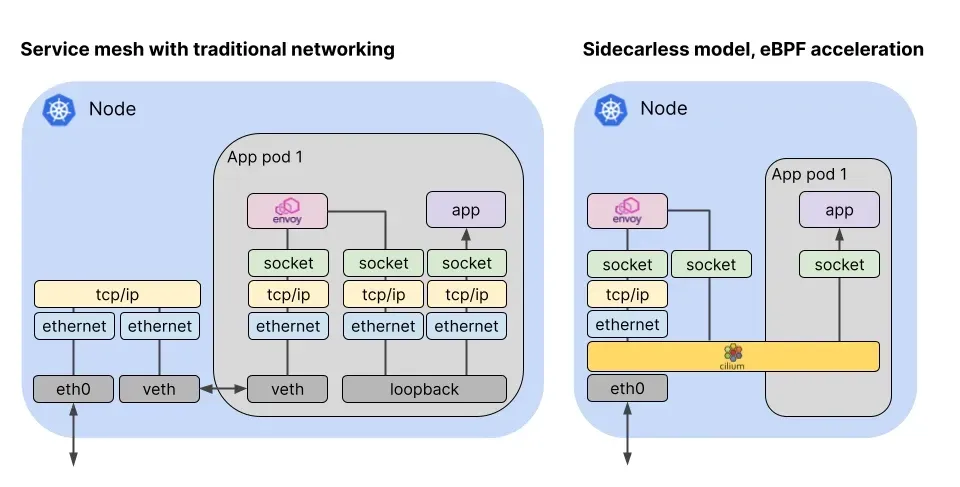
전통적인 Service Mesh(예: Istio)는 각 애플리케이션 Pod 옆에 사이드카(주로 Envoy 프록시)를 별도의 컨테이너로 배포하여, 모든 서비스 간 트래픽을 이 프록시가 중간에서 처리하는 구조입니다. 이 방식은 L7(애플리케이션 레이어, HTTP/gRPC 등)에서의 세밀한 트래픽 제어와 관찰성, 인증/인가, 트래픽 분할 등 다양한 기능을 제공합니다. 하지만, 모든 트래픽이 사이드카 프록시를 거치기 때문에 리소스 오버헤드가 발생하고, 네트워크 지연이 추가될 수 있습니다.
반면, Cilium은 eBPF(extended Berkeley Packet Filter)라는 커널 기술을 활용하여, L3/L4(네트워크/전송 계층, IP/TCP/UDP 등) 수준의 트래픽을 커널 레벨에서 매우 효율적으로 처리합니다. 즉, 별도의 프록시 컨테이너를 두지 않고, 커널 내부에서 직접 네트워크 정책, 로드밸런싱, 보안 정책 등을 적용할 수 있습니다. 이 덕분에 오버헤드가 적고, 네트워크 성능 저하 없이 서비스 메시의 핵심 기능(L3/L4 기반의 보안, 관찰성, 라우팅 등)을 제공할 수 있습니다.
Cilium도 L7(HTTP/gRPC 등) 수준의 트래픽 가시성이나 일부 제어 기능을 제공하지만, Istio와 같은 전통적인 Service Mesh에 비해 L7에서의 세밀한 트래픽 제어(예: 복잡한 라우팅, 트래픽 분할, 고급 인증/인가 등)는 상대적으로 제한적일 수 있습니다. 즉, Cilium은 L3/L4 계층에서의 효율성과 성능을 극대화하는 데 강점이 있고, L7에서는 기본적인 관찰성과 정책 적용을 지원합니다.
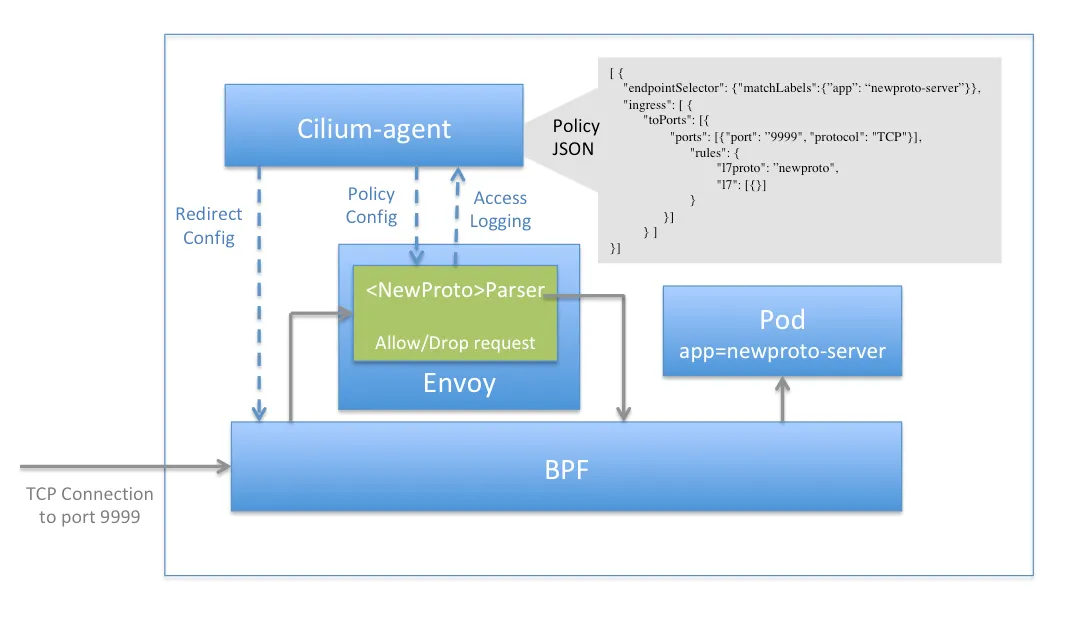
위 그림은 Cilium이 L7(애플리케이션 계층) 트래픽 관리 기능을 지원하는 구조를 보여줍니다. Cilium은 eBPF 기술을 활용하여 커널 레벨에서 L3/L4 트래픽을 효율적으로 처리할 뿐만 아니라, L7(HTTP/gRPC 등) 트래픽에 대해서도 가시성 및 일부 제어 기능을 제공합니다.
그림에서는 Cilium이 별도의 프록시 없이도 L7 트래픽을 인식하고, 정책 적용이나 관찰성(메트릭, 트레이싱 등) 기능을 제공할 수 있음을 시각적으로 나타내고 있습니다.
이를 통해 Cilium은 기존 사이드카 기반 서비스 메시와 달리, 오버헤드 없이 L7 트래픽 관리까지 지원할 수 있습니다.
k8s Ingress Support
Cilium은 표준 Kubernetes Ingress 리소스를 지원하며, ingressClassName을 cilium으로 설정하여 사용할 수 있습니다. 이를 통해 경로 기반 라우팅과 TLS 종료 기능을 제공합니다.
주요 특징
로드밸런서 모드
dedicated: Ingress별로 전용 로드밸런서 생성shared: 모든 Ingress 리소스가 공유 로드밸런서 사용- 모드 변경 시 LB IP가 변경되어 기존 활성 연결이 종료될 수 있음
필수 조건
- NodePort 활성화 (
nodePort.enabled=true또는kubeProxyReplacement=true) - L7 프록시 활성화 (
l7Proxy=true, 기본값) - LoadBalancer 타입 서비스 지원 환경 필요
Cilium Ingress의 차별점
아키텍처 차이
- 기존 Ingress 컨트롤러: Deployment/DaemonSet으로 설치, 별도 프록시 컨테이너
- Cilium Ingress: CNI와 밀접하게 통합, eBPF가 트래픽을 가로채어 Envoy로 투명 전달
TPROXY (Transparent Proxy) 메커니즘
- Cilium은 Envoy Proxy를 L7 데이터플레인으로 사용하지만, 단순 포트포워딩(REDIRECT)이 아닌 커널의 TPROXY 기능을 활용
- TPROXY 특징:
- 커널 netfilter/iptables에서 지원하는 특수 기능
- '투명 프록시' 역할: 클라이언트는 원래 목적지로 연결했다고 생각하지만, 실제로는 로컬 프록시(Envoy)로 트래픽이 리디렉션됨
- 원본 destination IP/Port, source IP/Port를 유지한 채 소켓 레벨에서 Envoy가 트래픽을 가로채어 처리
- Envoy가 "내가 80/443 포트에서 직접 리스닝한 것처럼" 패킷을 받을 수 있고, 그 과정은 클라이언트 입장에서 완전히 투명
동작 경로:
[Client] → [K8s Node:Ingress/Gateway Service Port]
↓ (eBPF Service LB)
[TPROXY] → [Envoy Proxy (Pod)]
↓ (L7 라우팅/정책 처리)
[eBPF] → [Backend Pod]
네트워크 정책 지원
- 노드별 Envoy 프록시에 CiliumNetworkPolicy 적용 가능
- Ingress 트래픽에 특별한
ingressidentity 할당 - 두 단계 정책 집행: world → ingress, ingress → backend
소스 IP 가시성
- 기본적으로
X-Forwarded-For헤더에 클라이언트 IP 추가 externalTrafficPolicy: Local설정 불필요 (Cilium이 자동 처리)- TLS Passthrough 시에는 Envoy IP가 소스로 표시됨
경로 타입 및 우선순위
- Exact: 정확한 경로 매칭
- ImplementationSpecific: 정규표현식 (Cilium에서 Regex로 해석)
- Prefix: URL 경로 접두사 매칭
/Prefix: 특별 처리로 항상 마지막
추가 기능
- Host Network Mode: 개발 환경에서 LoadBalancer 없이 직접 노출
- 노드 서브셋 배포: 특정 노드에만 Ingress 리스너 배포
- 다양한 애너테이션 지원: TLS, 리다이렉션, 헤더 수정 등
Cilium Ingress Support 관련 정보 확인
Cilium Ingress와 Cilium Gateway API는 동시 활성화가 불가능합니다.
이유는 두 기능이 모두 Envoy 및 동일한 리스너 포트(예: 80, 443 등)를 사용하여 트래픽을 처리하기 때문에, 동시에 활성화할 경우 포트 충돌 및 리소스 충돌이 발생하게 됩니다.
또한, Cilium의 내부 구현상 Ingress와 Gateway API가 각기 별도의 Envoy 인스턴스를 관리하지 않고, 동일한 데이터플레인(eBPF + Envoy)을 공유하기 때문에, 하나의 클러스터에서 두 기능을 동시에 사용할 수 없도록 설계되어 있습니다.
# cilium 설치 시 아래 파라미터 적용되어 있음
## --set ingressController.enabled=true
## --set ingressController.loadbalancerMode=shared
## --set loadBalancer.l7.backend=envoy \
cilium config view | grep -E '^loadbalancer|l7'
# ingress 에 예약된 내부 IP 확인 : node(cilium-envoy) 별로 존재
kubectl exec -it -n kube-system ds/cilium -- cilium ip list | grep ingress
# cilium-envoy 확인
kubectl get ds -n kube-system cilium-envoy -owide
kubectl get pod -n kube-system -l k8s-app=cilium-envoy -owide
kc describe pod -n kube-system -l k8s-app=cilium-envoy
ls -al /var/run/cilium/envoy/sockets
kubectl exec -it -n kube-system ds/cilium-envoy -- ls -al /var/run/cilium/envoy
kubectl exec -it -n kube-system ds/cilium-envoy -- cat /var/run/cilium/envoy/bootstrap-config.json > envoy.json
# envoy configmap 설정 내용 확인
kubectl -n kube-system get configmap cilium-envoy-config -o json \
| jq -r '.data["bootstrap-config.json"]' \
| jq . | grep admin.sock
tree /sys/fs/bpf
kubectl get svc,ep -n kube-system cilium-envoy
kubectl get svc,ep -n kube-system cilium-ingress
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# cilium config view | grep -E '^loadbalancer|l7'
enable-l7-proxy true # L7 프록시 활성화됨
loadbalancer-l7 envoy # L7 로드밸런서로 Envoy 사용
loadbalancer-l7-algorithm round_robin # L7 로드밸런싱 알고리즘: 라운드 로빈
loadbalancer-l7-ports # L7 포트 설정 (비어있음)
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# kubectl exec -it -n kube-system ds/cilium -- cilium ip list | grep ingress
172.20.0.166/32 reserved:ingress # k8s-ctr 노드용 Ingress 전용 IP
172.20.1.78/32 reserved:ingress # k8s-w1 노드용 Ingress 전용 IP
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# kubectl get ds -n kube-system cilium-envoy -owide
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE NODE SELECTOR AGE CONTAINERS IMAGES SELECTOR
cilium-envoy 2 2 2 2 2 kubernetes.io/os=linux 118m cilium-envoy quay.io/cilium/cilium-envoy:v1.34.4-1754895458-68cffdfa568b6b226d70a7ef81fc65dda3b890bf@sha256:247e908700012f7ef56f75908f8c965215c26a27762f296068645eb55450bda2 k8s-app=cilium-envoy
# DaemonSet으로 각 노드에 cilium-envoy 배포됨 (2개 노드에 각각 1개씩)
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# kubectl get pod -n kube-system -l k8s-app=cilium-envoy -owide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
cilium-envoy-4w8vp 1/1 Running 0 118m 192.168.10.100 k8s-ctr <none> <none> # 컨트롤 플레인 노드의 Envoy Pod
cilium-envoy-kfp2b 1/1 Running 0 116m 192.168.10.101 k8s-w1 <none> <none> # 워커 노드의 Envoy Pod
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# kc describe pod -n kube-system -l k8s-app=cilium-envoy
Name: cilium-envoy-4w8vp
Namespace: kube-system
Priority: 2000001000
Priority Class Name: system-node-critical # 시스템 노드 크리티컬 우선순위
Service Account: cilium-envoy
Node: k8s-ctr/192.168.10.100
Start Time: Tue, 19 Aug 2025 22:27:02 +0900
Labels: app.kubernetes.io/name=cilium-envoy
app.kubernetes.io/part-of=cilium
controller-revision-hash=bb65f66b
k8s-app=cilium-envoy
name=cilium-envoy
pod-template-generation=1
Annotations: container.apparmor.security.beta.kubernetes.io/cilium-envoy: unconfined
Status: Running
IP: 192.168.10.100
IPs:
IP: 192.168.10.100
Controlled By: DaemonSet/cilium-envoy
...
--
envoy-sockets:
Type: HostPath (bare host directory volume) # Envoy 소켓 파일용 호스트 볼륨
Path: /var/run/cilium/envoy/sockets
HostPathType: DirectoryOrCreate
envoy-artifacts:
Type: HostPath (bare host directory volume) # Envoy 아티팩트용 호스트 볼륨
Path: /var/run/cilium/envoy/artifacts
HostPathType: DirectoryOrCreate
envoy-config:
Type: ConfigMap (a volume populated by a ConfigMap) # Envoy 설정용 ConfigMap
Name: cilium-envoy-config
Optional: false
bpf-maps:
Type: HostPath (bare host directory volume) # eBPF 맵용 호스트 볼륨
Path: /sys/fs/bpf
HostPathType: DirectoryOrCreate
...
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# ls -al /var/run/cilium/envoy/sockets
total 0
drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 120 Aug 19 22:27 .
drwxr-xr-x 4 root root 80 Aug 19 22:27 ..
srw-rw---- 1 root 1337 0 Aug 19 22:27 access_log.sock # Envoy 액세스 로그용 Unix 소켓
srwxr-xr-x 1 root root 0 Aug 19 22:27 admin.sock # Envoy 관리 인터페이스용 Unix 소켓
drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 60 Aug 19 22:27 envoy # Envoy 관련 디렉토리
srw-rw---- 1 root 1337 0 Aug 19 22:27 xds.sock # XDS(Envoy Discovery Service) 통신용 Unix 소켓
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# kubectl exec -it -n kube-system ds/cilium-envoy -- ls -al /var/run/cilium/envoy
total 12
drwxrwxrwx 5 root root 4096 Aug 19 13:27 .
drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 4096 Aug 19 13:27 ..
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Aug 19 13:27 ..2025_08_19_13_27_02.588912407 # 설정 업데이트용 타임스탬프 디렉토리
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 31 Aug 19 13:27 ..data -> ..2025_08_19_13_27_02.588912407 # 현재 설정을 가리키는 심볼릭 링크
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 40 Aug 19 13:27 artifacts # Envoy 아티팩트 디렉토리
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 28 Aug 19 13:27 bootstrap-config.json -> ..data/bootstrap-config.json # Envoy 부트스트랩 설정 파일
drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 120 Aug 19 13:27 sockets # Unix 소켓 디렉토리
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# kubectl exec -it -n kube-system ds/cilium-envoy -- cat /var/run/cilium/envoy/bootstrap-config.json > envoy.json
# Envoy 부트스트랩 설정을 로컬 파일로 저장
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# kubectl -n kube-system get configmap cilium-envoy-config -o json \
| jq -r '.data["bootstrap-config.json"]' \
| jq . | grep admin.sock
"path": "/var/run/cilium/envoy/sockets/admin.sock" # Envoy 관리 인터페이스 소켓 경로
"path": "/var/run/cilium/envoy/sockets/admin.sock" # 중복 표시
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# tree /sys/fs/bpf
/sys/fs/bpf
├── cilium
│ ├── devices
│ │ ├── cilium_host
│ │ │ └── links
│ │ │ ├── cil_from_host
│ │ │ └── cil_to_host
... # eBPF 파일시스템 구조 - Cilium의 eBPF 프로그램들이 마운트됨
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# kubectl get svc,ep -n kube-system cilium-envoy
Warning: v1 Endpoints is deprecated in v1.33+; use discovery.k8s.io/v1 EndpointSlice
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/cilium-envoy ClusterIP None <none> 9964/TCP 121m # Headless 서비스 (ClusterIP: None)
NAME ENDPOINTS AGE
endpoints/cilium-envoy 192.168.10.100:9964,192.168.10.101:9964 121m # 각 노드의 Envoy Pod IP:포트
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# kubectl get svc,ep -n kube-system cilium-ingress
Warning: v1 Endpoints is deprecated in v1.33+; use discovery.k8s.io/v1 EndpointSlice
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/cilium-ingress LoadBalancer 10.96.200.152 <pending> 80:32679/TCP,443:31131/TCP 121m # Ingress용 LoadBalancer 서비스 (외부 IP 대기 중)
NAME ENDPOINTS AGE
endpoints/cilium-ingress 192.192.192.192:9999 121m # Ingress 엔드포인트 (가상 IP)
LB-IPAM 설정
LB-IPAM은 Load Balancer IP Address Management의 약자로, 쿠버네티스 클러스터 내에서 서비스 타입 LoadBalancer에 할당할 외부 IP 주소를 자동으로 관리하고 할당하는 기능입니다. Cilium에서는 LB-IPAM을 통해 L2(레이어2) 네트워크 기반으로 IP 풀을 정의하고, 서비스 생성 시 해당 풀에서 IP를 할당하여 외부에서 접근 가능한 LoadBalancer 서비스를 제공합니다. 이를 통해 클라우드 환경뿐만 아니라 온프레미스 환경에서도 외부 IP 할당 및 관리를 자동화할 수 있습니다.
cilium-l2announce는 Cilium에서 L2(레이어2) 네트워크 상에서 LoadBalancer 서비스의 외부 IP를 브로드캐스트(ARP/NDP)하여, 클러스터 외부에서도 해당 IP로 접근할 수 있도록 해주는 기능입니다. 즉, 클라우드 환경이 아닌 온프레미스 환경에서도 LoadBalancer 타입 서비스에 외부 IP를 할당하고, 이 IP를 네트워크에 알리는 역할을 합니다. 이를 통해 별도의 L2 로드밸런서 장비 없이도, 쿠버네티스 서비스에 외부에서 접근할 수 있게 됩니다.
여기서 중요한 점은, 외부 IP를 네트워크에 알리는 작업(ARP/NDP 브로드캐스트)을 클러스터 내 모든 노드가 동시에 수행하지 않고, leader 정책에 따라 특정 노드(leader)가 대표로 수행한다는 것입니다. leader는 쿠버네티스의 Lease 리소스를 활용해 선출되며, 해당 서비스의 외부 IP에 대한 L2 announce를 오직 leader 노드만 수행합니다. 이를 통해 네트워크 상의 충돌이나 중복 브로드캐스트를 방지할 수 있습니다.
아래 실행 결과를 보면, kubectl -n kube-system get lease | grep "cilium-l2announce" 명령어로 현재 leader 역할을 맡고 있는 노드를 확인할 수 있습니다. 또한, kubectl -n kube-system get lease/cilium-l2announce-kube-system-cilium-ingress -o yaml | yq 명령어를 통해 실제로 어떤 노드가 leader로 선출되어 있는지 Lease 리소스의 상세 정보를 확인할 수 있습니다. 이처럼 leader 정책을 통해 L2 announce의 일관성과 효율성을 보장합니다.
cilium config view | grep l2
cat << EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: "cilium.io/v2"
kind: CiliumLoadBalancerIPPool
metadata:
name: "cilium-lb-ippool"
spec:
blocks:
- start: "192.168.10.211"
stop: "192.168.10.215"
EOF
kubectl get ippool
kubectl get ippools -o jsonpath='{.items[*].status.conditions[?(@.type!="cilium.io/PoolConflict")]}' | jq
# L2 Announcement 정책 설정
cat << EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: "cilium.io/v2alpha1"
kind: CiliumL2AnnouncementPolicy
metadata:
name: policy1
spec:
interfaces:
- eth1
externalIPs: true
loadBalancerIPs: true
EOF
# 현재 리더 역할 노드 확인
kubectl -n kube-system get lease | grep "cilium-l2announce"
kubectl -n kube-system get lease/cilium-l2announce-kube-system-cilium-ingress -o yaml | yq
# K8S 클러스터 내부 LB EX-IP로 호출 가능
LBIP=$(kubectl get svc -n kube-system cilium-ingress -o jsonpath='{.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].ip}')
echo $LBIP
arping -i eth1 $LBIP -c 2
# k8s 외부 노드(router)에서 LB EX-IP로 호출 가능 확인
sshpass -p 'vagrant' ssh vagrant@router sudo arping -i eth1 $LBIP -c 2✅ 실행 결과 요약
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# cilium config view | grep l2
enable-l2-announcements true
enable-l2-neigh-discovery false
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# cat << EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: "cilium.io/v2"
kind: CiliumLoadBalancerIPPool
metadata:
name: "cilium-lb-ippool"
spec:
blocks:
- start: "192.168.10.211"
stop: "192.168.10.215"
EOF
ciliumloadbalancerippool.cilium.io/cilium-lb-ippool created
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# kubectl get ippool
NAME DISABLED CONFLICTING IPS AVAILABLE AGE
cilium-lb-ippool false False 4 4s
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# kubectl get ippools -o jsonpath='{.items[*].status.conditions[?(@.type!="cilium.io/PoolConflict")]}' | jq
{
"lastTransitionTime": "2025-08-19T15:36:48Z",
"message": "5",
"observedGeneration": 1,
"reason": "noreason",
"status": "Unknown",
"type": "cilium.io/IPsTotal"
}
{
"lastTransitionTime": "2025-08-19T15:36:48Z",
"message": "4",
"observedGeneration": 1,
"reason": "noreason",
"status": "Unknown",
"type": "cilium.io/IPsAvailable"
}
{
"lastTransitionTime": "2025-08-19T15:36:48Z",
"message": "1",
"observedGeneration": 1,
"reason": "noreason",
"status": "Unknown",
"type": "cilium.io/IPsUsed"
}
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# cat << EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: "cilium.io/v2alpha1"
kind: CiliumL2AnnouncementPolicy
metadata:
name: policy1
spec:
interfaces:
- eth1
externalIPs: true
loadBalancerIPs: true
EOF
ciliuml2announcementpolicy.cilium.io/policy1 created
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# kubectl -n kube-system get lease | grep "cilium-l2announce" #리더이기 때문에 무조건 k8s-w1으로 먼저 접속함
cilium-l2announce-kube-system-cilium-ingress k8s-w1
5s
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# kubectl -n kube-system get lease/cilium-l2announce-kube-system-cilium-ingress -o yaml | yq
{
"apiVersion": "coordination.k8s.io/v1",
"kind": "Lease",
"metadata": {
"creationTimestamp": "2025-08-19T15:37:05Z",
"name": "cilium-l2announce-kube-system-cilium-ingress",
"namespace": "kube-system",
"resourceVersion": "15737",
"uid": "3848e863-cee5-4c6a-ae62-ae517ad49238"
},
"spec": {
"acquireTime": "2025-08-19T15:37:05.787476Z",
"holderIdentity": "k8s-w1",
"leaseDurationSeconds": 15,
"leaseTransitions": 0,
"renewTime": "2025-08-19T15:37:13.829716Z"
}
}
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# LBIP=$(kubectl get svc -n kube-system cilium-ingress -o jsonpath='{.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].ip}')
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# echo $LBIP
192.168.10.211
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# arping -i eth1 $LBIP -c 2
ARPING 192.168.10.211
60 bytes from 08:00:27:88:d0:48 (192.168.10.211): index=0 time=777.541 usec
60 bytes from 08:00:27:88:d0:48 (192.168.10.211): index=1 time=577.625 usec
--- 192.168.10.211 statistics ---
2 packets transmitted, 2 packets received, 0% unanswered (0 extra)
rtt min/avg/max/std-dev = 0.578/0.678/0.778/0.100 ms
Ingress HTTP Example
다음으로 istio를 사용할 때 살펴본 book info 예제를 통해 Ingress HTTP를 실습해 봅니다.
# Deploy the Demo App : 공식 문서는 release-1.11 로 ARM CPU 에서 실패한다. 1.26 버전을 높여서 샘플 배포 할 것!
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/istio/istio/release-1.26/samples/bookinfo/platform/kube/bookinfo.yaml
# istio 와 다르게 사이드카 컨테이너가 없다 1/1 , NodePort와 LoadBalancer 서비스 없다.
kubectl get pod,svc,ep
#
kc describe ingressclasses.networking.k8s.io
kubectl get ingressclasses.networking.k8s.io
NAME CONTROLLER PARAMETERS AGE
cilium cilium.io/ingress-controller <none> 16m
# Basic ingress for istio bookinfo demo application, which can be found in below
cat << EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: basic-ingress
namespace: default
spec:
ingressClassName: cilium
rules:
- http:
paths:
- backend:
service:
name: details
port:
number: 9080
path: /details
pathType: Prefix
- backend:
service:
name: productpage
port:
number: 9080
path: /
pathType: Prefix
EOF
# Adress 는 cilium-ingress LoadBalancer 의 EX-IP
kubectl get svc -n kube-system cilium-ingress
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
cilium-ingress LoadBalancer 10.96.154.81 192.168.10.211 80:32046/TCP,443:31695/TCP 154m
kubectl get ingress
NAME CLASS HOSTS ADDRESS PORTS AGE
basic-ingress cilium * 192.168.10.211 80 33s
kc describe ingress
Host Path Backends
---- ---- --------
*
/details details:9080 (172.20.1.59:9080)
/ productpage:9080 (172.20.1.202:9080)
# 호출 확인
LBIP=$(kubectl get svc -n kube-system cilium-ingress -o jsonpath='{.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].ip}')
echo $LBIP
# 실패하는 호출이 있는가?
curl -so /dev/null -w "%{http_code}\n" http://$LBIP/
curl -so /dev/null -w "%{http_code}\n" http://$LBIP/details/1
curl -so /dev/null -w "%{http_code}\n" http://$LBIP/ratings
# Access the Bookinfo application
curl "http://$LBIP/productpage?u=normal"
# 모니터링
cilium hubble port-forward&
hubble observe -f -t l7
or
hubble observe -f --identity ingress
...
# productpage-v1 파드가 배포된 노드 확인
kubectl get pod -l app=productpage -owide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
productpage-v1-5b69f9996c-5rrkz 1/1 Running 0 13m 172.20.1.110 k8s-w1 <none> <none>
# 해당 노드(k8s-w1)에서 veth 인터페이스 정보 확인
PROID=172.20.1.110
ip route |grep $PROID
PROVETH=lxc80e7403fef4e
# ngrep 로 veth 트래픽 캡쳐 : productpage 는 9080 TCP Port 사용
ngrep -tW byline -d $PROVETH '' 'tcp port 9080'
Cilium Service Mesh 는 sidecar가 붙지 않습니다!!
✅ 실행 결과 요약
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# kubectl get pod,svc,ep
Warning: v1 Endpoints is deprecated in v1.33+; use discovery.k8s.io/v1 EndpointSlice
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/curl-pod 1/1 Running 0 89m # 테스트용 curl Pod
pod/details-v1-766844796b-2mbl9 1/1 Running 0 6m56s # Bookinfo details 서비스 Pod
pod/productpage-v1-54bb874995-m4cp8 1/1 Running 0 6m56s # Bookinfo productpage 서비스 Pod
pod/ratings-v1-5dc79b6bcd-qgqg9 1/1 Running 0 6m56s # Bookinfo ratings 서비스 Pod
pod/reviews-v1-598b896c9d-kv7np 1/1 Running 0 6m56s # Bookinfo reviews v1 Pod
pod/reviews-v2-556d6457d-sps55 1/1 Running 0 6m56s # Bookinfo reviews v2 Pod
pod/reviews-v3-564544b4d6-dmmgf 1/1 Running 0 6m56s # Bookinfo reviews v3 Pod
pod/webpod-697b545f57-f9dpx 1/1 Running 0 89m # 기존 webpod v1
pod/webpod-697b545f57-wwjxp 1/1 Running 0 89m # 기존 webpod v2
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/details ClusterIP 10.96.183.111 <none> 9080/TCP 6m56s # details 서비스 (ClusterIP)
service/kubernetes ClusterIP 10.96.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 149m # Kubernetes API 서버
service/productpage ClusterIP 10.96.58.11 <none> 9080/TCP 6m56s # productpage 서비스 (ClusterIP)
service/ratings ClusterIP 10.96.136.177 <none> 9080/TCP 6m56s # ratings 서비스 (ClusterIP)
service/reviews ClusterIP 10.96.85.30 <none> 9080/TCP 6m56s # reviews 서비스 (ClusterIP)
service/webpod ClusterIP 10.96.134.235 <none> 80/TCP 89m # 기존 webpod 서비스
NAME ENDPOINTS AGE
endpoints/details 172.20.1.116:9080 6m56s # details Pod IP:포트
endpoints/kubernetes 192.168.10.100:6443 149m # API 서버 엔드포인트
endpoints/productpage 172.20.1.110:9080 6m56s # productpage Pod IP:포트
endpoints/ratings 172.20.1.217:9080 6m56s # ratings Pod IP:포트
endpoints/reviews 172.20.1.148:9080,172.20.1.190:9080,172.20.1.218:9080 6m56s # reviews v1,v2,v3 Pod IP:포트들
endpoints/webpod 172.20.0.128:80,172.20.1.140:80 89m # webpod v1,v2 Pod IP:포트들
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# kc describe ingressclasses.networking.k8s.io
Name: cilium
Labels: app.kubernetes.io/managed-by=Helm
Annotations: meta.helm.sh/release-name: cilium
meta.helm.sh/release-namespace: kube-system
Controller: cilium.io/ingress-controller # Cilium Ingress 컨트롤러
Events: <none>
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# kubectl get ingressclasses.networking.k8s.io
NAME CONTROLLER PARAMETERS AGE
cilium cilium.io/ingress-controller <none> 149m # Cilium Ingress 클래스 (149분 전 생성)
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# kubectl get svc -n kube-system cilium-ingress
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
cilium-ingress LoadBalancer 10.96.200.152 192.168.10.211 80:32679/TCP,443:31131/TCP 150m # Cilium Ingress LoadBalancer 서비스 (외부 IP: 192.168.10.211)
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# kubectl get ingress
NAME CLASS HOSTS ADDRESS PORTS AGE
basic-ingress cilium * 192.168.10.211 80 12s # basic-ingress 생성됨 (12초 전, 외부 IP: 192.168.10.211)
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# kc describe ingress
Name: basic-ingress
Labels: <none>
Namespace: default
Address: 192.168.10.211 # Ingress 외부 IP 주소
Ingress Class: cilium # Cilium Ingress 클래스 사용
Default backend: <default>
Rules:
Host Path Backends
---- ---- --------
*
/details details:9080 (172.20.1.116:9080) # /details 경로 → details 서비스
/ productpage:9080 (172.20.1.110:9080) # / 경로 → productpage 서비스
Annotations: <none>
Events: <none>
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# LBIP=$(kubectl get svc -n kube-system cilium-ingress -o jsonpath='{.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].ip}')
# LoadBalancer IP를 변수에 저장
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# echo $LBIP
192.168.10.211 # LoadBalancer 외부 IP
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# curl -so /dev/null -w "%{http_code}\n" http://$LBIP/
200 # 루트 경로 접근 성공 (productpage 서비스)
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# curl -so /dev/null -w "%{http_code}\n" http://$LBIP/details/1
200 # /details 경로 접근 성공 (details 서비스)
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# curl -so /dev/null -w "%{http_code}\n" http://$LBIP/ratings
404 # /ratings 경로 접근 실패 (Ingress에 정의되지 않은 경로)
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# curl "http://$LBIP/productpage?u=normal"
# Bookinfo 애플리케이션 접근 테스트 (정상 사용자)
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Simple Bookstore App</title>
<script src="static/tailwind/tailwind.css"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
... # Bookinfo 애플리케이션 HTML 응답 (정상 동작 확인)
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# kubectl get pod -l app=productpage -owide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
productpage-v1-54bb874995-m4cp8 1/1 Running 0 10m 172.20.1.110 k8s-w1 <none> <none> # productpage Pod가 k8s-w1 노드에 배포됨 (IP: 172.20.1.110)
# w1 에서 확인
root@k8s-w1:~# PROID=172.20.1.110
# productpage Pod IP 설정
root@k8s-w1:~# ip route |grep $PROID
172.20.1.110 dev lxc5b1ea7c0b527 proto kernel scope link
# productpage Pod의 veth 인터페이스 확인 (lxc5b1ea7c0b527)
root@k8s-w1:~# PROVETH=lxc5b1ea7c0b527
# veth 인터페이스명을 변수에 저장
root@k8s-w1:~# ngrep -tW byline -d $PROVETH '' 'tcp port 9080'
lxc5b1ea7c0b527: no IPv4 address assigned: Cannot assign requested address
interface: lxc5b1ea7c0b527
filter: ( tcp port 9080 ) and ((ip || ip6) || (vlan && (ip || ip6)))
#### 외부 IP
T 2025/08/20 01:35:57.509938 10.0.2.15:40346 -> 172.20.1.110:9080 [AP] #4
GET / HTTP/1.1.
host: 192.168.10.211.
user-agent: curl/8.5.0.
accept: */*.
x-forwarded-for: 192.168.10.200. #x-forwraded-for 클라이언트 IP가 담겨서 옴
x-forwarded-proto: http.
x-envoy-internal: true.
x-request-id: 158c8f13-1802-4785-9394-985239d4850f.
x-forwarded-for는 프록시(예: Ingress, LoadBalancer, Envoy 등)를 거쳐 전달된 HTTP 요청에서 원래 클라이언트의 IP 주소를 담는 HTTP 헤더입니다. 즉, 실제로 요청을 보낸 사용자의 IP를 백엔드 서비스가 알 수 있도록 해줍니다. 여러 프록시를 거칠 경우, 각 프록시가 이 헤더에 자신의 앞단 클라이언트 IP를 추가합니다.

Cilium Ingress를 통한 외부 접근 테스트: LoadBalancer IP (192.168.10.211)로 Bookinfo 애플리케이션에 접근하여 정상적으로 응답을 받는 것을 확인했습니다.

Hubble을 통한 L7 트래픽 모니터링: HTTP 요청/응답, 헤더 정보, 상태 코드 등 애플리케이션 레벨의 상세한 트래픽 정보를 실시간으로 관찰 가능합니다.
ingress-Nginx 설치 및 설정
Ingress nginx도 함께 사용할 수 있습니다.
# Ingress-Nginx 컨트롤러 설치
helm repo add ingress-nginx https://kubernetes.github.io/ingress-nginx
helm install ingress-nginx ingress-nginx/ingress-nginx --create-namespace -n ingress-nginx
# 확인
kubectl get all -n ingress-nginx
kc describe svc -n ingress-nginx ingress-nginx-controller
kubectl get svc -n ingress-nginx
kubectl get ingressclasses.networking.k8s.io
NAME CONTROLLER PARAMETERS AGE
cilium cilium.io/ingress-controller <none> 18m
nginx k8s.io/ingress-nginx <none> 22s
# ingress 설정
cat << EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: webpod-ingress-nginx
namespace: default
spec:
ingressClassName: nginx
rules:
- host: nginx.webpod.local
http:
paths:
- backend:
service:
name: webpod
port:
number: 80
path: /
pathType: Prefix
EOF
# ingress LB EX-IP 할당 까지 다소 시간 소요..
kubectl get ingress -w
NAME CLASS HOSTS ADDRESS PORTS AGE
basic-ingress cilium * 192.168.10.211 80 3m19s
webpod-ingress-nginx nginx nginx.webpod.local 192.168.10.212 80 11m
#
LB2IP=$(kubectl get svc -n ingress-nginx ingress-nginx-controller -o jsonpath='{.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].ip}')
curl $LB2IP
<html>
<head><title>404 Not Found</title></head>
<body>
<center><h1>404 Not Found</h1></center>
<hr><center>nginx</center>
</body>
</html>
curl -H "Host: nginx.webpod.local" $LB2IP
Hostname: webpod-697b545f57-f9dpx
IP: 127.0.0.1
IP: ::1
IP: 172.20.1.140
IP: fe80::e098:63ff:fefa:cd8e
RemoteAddr: 172.20.1.36:39490
GET / HTTP/1.1
Host: nginx.webpod.local
User-Agent: curl/8.5.0
Accept: */*
X-Forwarded-For: 192.168.10.100
X-Forwarded-Host: nginx.webpod.local
X-Forwarded-Port: 80
X-Forwarded-Proto: http
X-Forwarded-Scheme: http
X-Real-Ip: 192.168.10.100
X-Request-Id: 4fd11f60046be2191f915f224d395103
X-Scheme: httpDedicated mode
- Shared Mode:
여러 Ingress 리소스가 하나의 Ingress Controller(예: cilium-ingress)를 공유하여, 동일한 LoadBalancer IP(External IP)를 함께 사용합니다. 이 경우, 여러 Ingress가 동일한 IP와 포트를 통해 트래픽을 받아 경로(path) 또는 호스트(host) 기반으로 라우팅됩니다. 일반적으로 기본 cilium-ingress가 Shared Mode로 동작합니다. - Dedicated Mode:
Ingress Controller가 별도의 LoadBalancer IP(External IP) 또는 특정 IPPool, 네트워크 인터페이스에 독립적으로 바인딩되어 동작합니다. 즉, 각 Ingress Controller가 자신만의 외부 IP를 독점적으로 할당받아 사용하므로, 여러 Ingress Controller가 클러스터 내에서 서로 충돌 없이 각자의 역할을 수행할 수 있습니다.
예를 들어, 내부 서비스용 Ingress Controller와 외부 서비스용 Ingress Controller를 분리하여 각각 다른 IPPool을 사용하도록 설정할 수 있습니다. 이를 통해 트래픽 분리, 보안 강화, 네트워크 정책 세분화 등 다양한 운영 시나리오에 대응할 수 있습니다.
cat << EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: webpod-ingress
namespace: default
annotations:
ingress.cilium.io/loadbalancer-mode: dedicated
spec:
ingressClassName: cilium
rules:
- http:
paths:
- backend:
service:
name: webpod
port:
number: 80
path: /
pathType: Prefix
EOF
#
kc describe ingress webpod-ingress
kubectl get ingress
kubectl get svc,ep cilium-ingress-webpod-ingress
# LB EX-IP에 대한 L2 Announcement 의 Leader 노드 확인
kubectl get lease -n kube-system | grep ingress
# webpod 파드 IP 확인
kubectl get pod -l app=webpod -owide✅ 실행 결과 요약
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# kubectl get ingress
NAME CLASS HOSTS ADDRESS PORTS AGE
basic-ingress cilium * 192.168.10.211 80 46h
webpod-ingress cilium * 192.168.10.213 80 11s # 별도의 아이피를 사용
webpod-ingress-nginx nginx nginx.webpod.local 192.168.10.212 80 45h
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# kubectl get svc,ep cilium-ingress-webpod-ingress
Warning: v1 Endpoints is deprecated in v1.33+; use discovery.k8s.io/v1 EndpointSlice
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/cilium-ingress-webpod-ingress LoadBalancer 10.96.127.231 192.168.10.213 80:31570/TCP,443:31738/TCP 18s
NAME ENDPOINTS AGE
endpoints/cilium-ingress-webpod-ingress 192.192.192.192:9999 18s
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# kubectl get lease -n kube-system | grep ingress
cilium-l2announce-default-cilium-ingress-webpod-ingress k8s-w1
cilium-l2announce-ingress-nginx-ingress-nginx-controller k8s-w1
cilium-l2announce-kube-system-cilium-ingress k8s-w1
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# kubectl get pod -l app=webpod -owide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
webpod-697b545f57-f9dpx 1/1 Running 0 47h 172.20.1.140 k8s-w1 <none> <none>
webpod-697b545f57-wwjxp 1/1 Running 0 47h 172.20.0.128 k8s-ctr <none> <none>Ingress and Network Policy Example
CiliumClusterwideNetworkPolicy는 Cilium에서 제공하는 클러스터 전체에 적용되는 네트워크 정책 리소스입니다.
기존의 Kubernetes NetworkPolicy가 네임스페이스 단위로만 적용되는 것과 달리,
CiliumClusterwideNetworkPolicy는 여러 네임스페이스에 걸쳐 일관된 네트워크 보안 정책을 적용할 수 있습니다.
# 클러스터 전체(모든 네임스페이스)에 적용되는 정책 : 참고로 아래 정책 적용 후 Hubble-ui 로 접속 불가!
cat << EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: "cilium.io/v2"
kind: CiliumClusterwideNetworkPolicy
metadata:
name: "external-lockdown" #클러스터 외주 요청 락다운 시킴
spec:
description: "Block all the traffic originating from outside of the cluster"
endpointSelector: {}
ingress:
- fromEntities:
- cluster
EOF
kubectl get ciliumclusterwidenetworkpolicy
#
curl --fail -v http://"$LBIP"/details/1
< HTTP/1.1 403 Forbidden
#
hubble observe -f --identity ingress
## k8s-ctr 에서 curl 실행 시
Aug 16 14:02:01.011: 127.0.0.1:58328 (ingress) -> 127.0.0.1:14485 (world) http-request DROPPED (HTTP/1.1 GET http://192.168.10.211/details/1)
Aug 16 14:02:01.011: 127.0.0.1:58328 (ingress) <- 127.0.0.1:14485 (world) http-response FORWARDED (HTTP/1.1 403 0ms (GET http://192.168.10.211/details/1))
## router 에서 curl 실행 시
Aug 16 14:03:35.580: 192.168.10.200:56904 (ingress) -> kube-system/cilium-ingress:80 (world) http-request DROPPED (HTTP/1.1 GET http://192.168.10.211/)
Aug 16 14:03:35.580: 192.168.10.200:56904 (ingress) <- kube-system/cilium-ingress:80 (world) http-response FORWARDED (HTTP/1.1 403 0ms (GET http://192.168.10.211/))
# 정의된 CIDR의 모든 트레픽 허용.
cat << EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: "cilium.io/v2"
kind: CiliumClusterwideNetworkPolicy
metadata:
name: "allow-cidr"
spec:
description: "Allow all the traffic originating from a specific CIDR"
endpointSelector:
matchExpressions:
- key: reserved:ingress
operator: Exists
ingress:
- fromCIDRSet:
# Please update the CIDR to match your environment
- cidr: 192.168.10.200/32
- cidr: 127.0.0.1/32
EOF
# 요청 성공! : k8s-ctr , router 모두 가능
curl --fail -v http://"$LBIP"/details/1
sshpass -p 'vagrant' ssh vagrant@router "curl -s --fail -v http://"$LBIP"/details/1"
# Default Deny Ingress Policy : DNS쿼리와 kube-system내의 파드 제외 to deny all traffic by default
cat << EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: cilium.io/v2
kind: CiliumClusterwideNetworkPolicy
metadata:
name: "default-deny"
spec:
description: "Block all the traffic (except DNS) by default"
egress:
- toEndpoints:
- matchLabels:
io.kubernetes.pod.namespace: kube-system
k8s-app: kube-dns
toPorts:
- ports:
- port: '53'
protocol: UDP
rules:
dns:
- matchPattern: '*'
endpointSelector:
matchExpressions:
- key: io.kubernetes.pod.namespace
operator: NotIn
values:
- kube-system
EOF
kubectl get ciliumclusterwidenetworkpolicy
# 요청
curl --fail -v http://"$LBIP"/details/1
sshpass -p 'vagrant' ssh vagrant@router "curl -s --fail -v http://"$LBIP"/details/1"
# ingress 를 통해서 인입 시 허용
cat << EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: cilium.io/v2
kind: CiliumClusterwideNetworkPolicy
metadata:
name: allow-ingress-egress
spec:
description: "Allow all the egress traffic from reserved ingress identity to any endpoints in the cluster"
endpointSelector:
matchExpressions:
- key: reserved:ingress
operator: Exists
egress:
- toEntities:
- cluster
EOF
kubectl get ciliumclusterwidenetworkpolicy
#
curl --fail -v http://"$LBIP"/details/1
sshpass -p 'vagrant' ssh vagrant@router "curl -s --fail -v http://"$LBIP"/details/1"
# 정책 삭제
kubectl delete CiliumClusterwideNetworkPolicy --all✅ 실행 결과 요약
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# kubectl get ciliumclusterwidenetworkpolicy
NAME VALID
external-lockdown True
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# curl --fail -v http://"$LBIP"/details/1
curl: (22) The requested URL returned error: 403
#클러스터 외주 요청 락다운 시킴
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# hubble observe -f --identity ingress
# ctr 요청
Aug 21 14:26:30.950: 127.0.0.1:47032 (ingress) -> 127.0.0.1:15930 (world) http-request DROPPED (HTTP/1.1 GET http://192.168.10.211/details/1)
Aug 21 14:26:30.950: 127.0.0.1:47032 (ingress) <- 127.0.0.1:15930 (world) http-response FORWARDED (HTTP/1.1 403 0ms (GET http://192.168.10.211/details/1))
# 라우터에서 요청
Aug 21 14:27:06.809: 192.168.10.200:49188 (ingress) -> kube-system/cilium-ingress:80 (world) http-request DROPPED (HTTP/1.1 GET http://192.168.10.211/details/1)
Aug 21 14:27:06.809: 192.168.10.200:49188 (ingress) <- kube-system/cilium-ingress:80 (world) http-response FORWARDED (HTTP/1.1 403 0ms (GET http://192.168.10.211/details/1))
# 정의된 CIDR의 모든 트레픽 허용
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# hubble observe -f --identity ingress
# ctr 요청
Aug 21 14:30:11.109: 172.20.0.166:36991 (ingress) -> default/details-v1-766844796b-2mbl9:9080 (ID:29027) policy-verdict:L3-Only INGRESS ALLOWED (TCP Flags: SYN)
...
Aug 21 14:30:11.125: 127.0.0.1:59582 (ingress) <- default/details-v1-766844796b-2mbl9:9080 (ID:29027) http-response FORWARDED (HTTP/1.1 200 19ms (GET http://192.168.10.211/details/1))
# 라우터에서 요청
Aug 21 14:30:41.171: 172.20.0.166:36991 (ingress) <- default/details-v1-766844796b-2mbl9:9080 (ID:29027) to-network FORWARDED (TCP Flags: ACK, FIN)
Aug 21 14:30:41.172: 172.20.0.166:36991 (ingress) -> default/details-v1-766844796b-2mbl9:9080 (ID:29027) to-endpoint FORWARDED (TCP Flags: ACK, FIN)
# Default Deny Ingress Policy : DNS쿼리와 kube-system내의 파드 제외 to deny all traffic by default
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# kubectl get ciliumclusterwidenetworkpolicy
NAME VALID
allow-cidr True
default-deny True
external-lockdown True
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# hubble observe -f --identity ingress
# ctr 요청
Aug 21 14:33:39.547: 127.0.0.1:54702 (ingress) -> 127.0.0.1:15930 (ID:16777218) http-request DROPPED (HTTP/1.1 GET http://192.168.10.211/details/1)
Aug 21 14:33:39.547: 127.0.0.1:54702 (ingress) <- 127.0.0.1:15930 (ID:16777218) http-response FORWARDED (HTTP/1.1 403 0ms (GET http://192.168.10.211/details/1))
# 라우터에서 요청
Aug 21 14:33:55.343: 192.168.10.200:59416 (ingress) -> kube-system/cilium-ingress:80 (world) http-request DROPPED (HTTP/1.1 GET http://192.168.10.211/details/1)
Aug 21 14:33:55.343: 192.168.10.200:59416 (ingress) <- kube-system/cilium-ingress:80 (world) http-response FORWARDED (HTTP/1.1 403 0ms (GET http://192.168.10.211/details/1))
ciliumclusterwidenetworkpolicy.cilium.io/allow-ingress-egress created
# ingress 를 통해서 인입 시 허용
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# kubectl get ciliumclusterwidenetworkpolicy
NAME VALID
allow-cidr True
allow-ingress-egress True
default-deny True
external-lockdown True
# ingress 를 통하는 내 외부 모두 통신이 잘 되는 것을 확인
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# hubble observe -f --identity ingress
...
Aug 21 14:35:53.311: 10.0.2.15:34166 (ingress) -> default/details-v1-766844796b-2mbl9:9080 (ID:29027) to-endpoint FORWARDED (TCP Flags: SYN)
Aug 21 14:35:53.312: 10.0.2.15:34166 (ingress) -> default/details-v1-766844796b-2mbl9:9080 (ID:29027) to-endpoint FORWARDED (TCP Flags: ACK)
Aug 21 14:35:53.312: 10.0.2.15:34166 (ingress) -> default/details-v1-766844796b-2mbl9:9080 (ID:29027) to-endpoint FORWARDED (TCP Flags: ACK, PSH)
Aug 21 14:35:53.312: 192.168.10.200:40130 (ingress) -> default/details-v1-766844796b-2mbl9:9080 (ID:29027) http-request FORWARDED (HTTP/1.1 GET http://192.168.10.211/details/1)
Aug 21 14:35:53.316: 192.168.10.200:40130 (ingress) <- default/details-v1-766844796b-2mbl9:9080 (ID:29027) http-response FORWARDED (HTTP/1.1 200 6ms (GET http://192.168.10.211/details/1))Ingress Path Types Example
# Apply the base definitions
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cilium/cilium/main/examples/kubernetes/servicemesh/ingress-path-types.yaml
# 확인
kubectl get -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cilium/cilium/main/examples/kubernetes/servicemesh/ingress-path-types.yaml
# Apply the Ingress
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cilium/cilium/main/examples/kubernetes/servicemesh/ingress-path-types-ingress.yaml
# 확인
kc describe ingress multiple-path-types
# 호출 확인
export PATHTYPE_IP=`k get ing multiple-path-types -o json | jq -r '.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].ip'`
curl -s -H "Host: pathtypes.example.com" http://$PATHTYPE_IP/ | jq
# 파드명 이름 확인
kubectl get pod | grep path
exactpath-7488f8c6c6-pd4pc 1/1 Running 0 7m25s
implpath-7d8bf85676-f7k5s 1/1 Running 0 7m25s
implpath2-56c97c8556-mtnnm 1/1 Running 0 7m25s
prefixpath-5d6b989d4-w4qv2 1/1 Running 0 7m25s
prefixpath2-b7c7c9568-mkv8d 1/1 Running 0 7m25s
# Should show prefixpath
curl -s -H "Host: pathtypes.example.com" http://$PATHTYPE_IP/ | grep -E 'path|pod'
# Should show exactpath
curl -s -H "Host: pathtypes.example.com" http://$PATHTYPE_IP/exact | grep -E 'path|pod'
# Should show prefixpath2
curl -s -H "Host: pathtypes.example.com" http://$PATHTYPE_IP/prefix | grep -E 'path|pod'
# Should show implpath
curl -s -H "Host: pathtypes.example.com" http://$PATHTYPE_IP/impl | grep -E 'path|pod'
# Should show implpath2
curl -s -H "Host: pathtypes.example.com" http://$PATHTYPE_IP/implementation | grep -E 'path|pod'
# 삭제
kubectl delete -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cilium/cilium/main/examples/kubernetes/servicemesh/ingress-path-types.yaml
kubectl delete -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cilium/cilium/main/examples/kubernetes/servicemesh/ingress-path-types-ingress.yaml
✅ 실행 결과 요약
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# kubectl get -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cilium/cilium/main/examples/kubernetes/servicemesh/ingress-path-types.yaml
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment.apps/exactpath 1/1 1 1 18s
deployment.apps/prefixpath 1/1 1 1 18s
deployment.apps/prefixpath2 1/1 1 1 18s
deployment.apps/implpath 1/1 1 1 18s
deployment.apps/implpath2 1/1 1 1 18s
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/prefixpath ClusterIP 10.96.2.108 <none> 80/TCP 18s
service/prefixpath2 ClusterIP 10.96.65.59 <none> 80/TCP 18s
service/exactpath ClusterIP 10.96.199.191 <none> 80/TCP 18s
service/implpath ClusterIP 10.96.187.177 <none> 80/TCP 18s
service/implpath2 ClusterIP 10.96.127.241 <none> 80/TCP 18s
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# kc describe ingress multiple-path-types
Name: multiple-path-types
Labels: <none>
Namespace: default
Address: 192.168.10.211
Ingress Class: cilium
Default backend: <default>
Rules:
Host Path Backends
---- ---- --------
pathtypes.example.com
/exact exactpath:80 (172.20.1.72:3000)
/ prefixpath:80 (172.20.1.227:3000)
/prefix prefixpath2:80 (172.20.1.21:3000)
/impl implpath:80 (172.20.1.62:3000)
/impl.+ implpath2:80 (172.20.1.34:3000)
Annotations: <none>
Events: <none>
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# export PATHTYPE_IP=`k get ing multiple-path-types -o json | jq -r '.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].ip'`
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# curl -s -H "Host: pathtypes.example.com" http://$PATHTYPE_IP/ | jq
{
"path": "/",
"host": "pathtypes.example.com",
"method": "GET",
"proto": "HTTP/1.1",
"headers": {
"Accept": [
"*/*"
],
"User-Agent": [
"curl/8.5.0"
],
"X-Envoy-Internal": [
"true"
],
"X-Forwarded-For": [
"10.0.2.15"
],
"X-Forwarded-Proto": [
"http"
],
"X-Request-Id": [
"ae160a0d-6c31-457b-ac76-687ea06a18bf"
]
},
"namespace": "default",
"ingress": "",
"service": "",
"pod": "prefixpath-5d6b989d4-cdpzv"
}
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# kubectl get pod | grep path
exactpath-7488f8c6c6-w9msh 1/1 Running 0 98s
implpath-7d8bf85676-ctm9m 1/1 Running 0 98s
implpath2-56c97c8556-72sdn 1/1 Running 0 98s
prefixpath-5d6b989d4-cdpzv 1/1 Running 0 98s
prefixpath2-b7c7c9568-rs9v7 1/1 Running 0 98s
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# curl -s -H "Host: pathtypes.example.com" http://$PATHTYPE_IP/ | grep -E 'path|pod'
"path": "/",
"host": "pathtypes.example.com",
"pod": "prefixpath-5d6b989d4-cdpzv"
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# curl -s -H "Host: pathtypes.example.com" http://$PATHTYPE_IP/exact | grep -E 'path|pod'
"path": "/exact",
"host": "pathtypes.example.com",
"pod": "exactpath-7488f8c6c6-w9msh"
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# curl -s -H "Host: pathtypes.example.com" http://$PATHTYPE_IP/prefix | grep -E 'path|pod'
"path": "/prefix",
"host": "pathtypes.example.com",
"pod": "prefixpath2-b7c7c9568-rs9v7"
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# curl -s -H "Host: pathtypes.example.com" http://$PATHTYPE_IP/impl | grep -E 'path|pod'
"path": "/impl",
"host": "pathtypes.example.com",
"pod": "implpath-7d8bf85676-ctm9m"
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# curl -s -H "Host: pathtypes.example.com" http://$PATHTYPE_IP/implementation | grep -E 'path|pod'
"path": "/implementation",
"host": "pathtypes.example.com",
"pod": "implpath2-56c97c8556-72sdn"TLS Termination
TLS 인증서와 개인키 생성 : mkcert - Github
mkcert는 로컬 개발 환경에서 신뢰할 수 있는 인증서를 손쉽게 생성해주는 도구입니다. 별도의 복잡한 설정 없이 사용할 수 있습니다.
# ===== TLS 인증서 생성 및 설정 과정 =====
# 1. mkcert 도구 설치 (로컬 개발용 SSL 인증서 생성 도구)
# For demonstration purposes we will use a TLS certificate signed by a made-up, self-signed certificate authority (CA).
# One easy way to do this is with mkcert. We want a certificate that will validate bookinfo.cilium.rocks and hipstershop.cilium.rocks, as these are the host names used in this example.
apt install mkcert -y # mkcert 패키지 설치
mkcert -h # mkcert 도움말 확인
# 2. 와일드카드 SSL 인증서 생성 (*.cilium.rocks 도메인용)
mkcert '*.cilium.rocks' # 와일드카드 인증서로 모든 cilium.rocks 서브도메인 지원
# 3. 생성된 인증서 파일 확인
ls -l *.pem
-rw------- 1 root root 1708 Aug 17 12:11 _wildcard.cilium.rocks-key.pem # 개인키 파일
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1452 Aug 17 12:11 _wildcard.cilium.rocks.pem # 공개 인증서 파일
# 4. 인증서 상세 정보 확인
openssl x509 -in _wildcard.cilium.rocks.pem -text -noout
Issuer: O = mkcert development CA, OU = root@k8s-ctr, CN = mkcert root@k8s-ctr # 발급자 정보
Validity
Not Before: Aug 17 03:11:30 2025 GMT # 유효기간 시작
Not After : Nov 17 03:11:30 2027 GMT # 유효기간 종료
Subject: O = mkcert development certificate, OU = root@k8s-ctr # 주체 정보
...
X509v3 extensions:
X509v3 Key Usage: critical
Digital Signature, Key Encipherment # 디지털 서명 및 키 암호화 용도
X509v3 Extended Key Usage:
TLS Web Server Authentication # TLS 웹서버 인증용
X509v3 Authority Key Identifier:
7E:20:AF:5F:00:4A:C8:6B:D6:44:C5:4F:32:C0:ED:FB:3C:0D:30:00
X509v3 Subject Alternative Name:
DNS:*.cilium.rocks # 와일드카드 도메인 지정
# 5. 개인키 정보 확인 (RSA 2048비트)
openssl rsa -in _wildcard.cilium.rocks-key.pem -text -noout
Private-Key: (2048 bit, 2 primes) # 2048비트 RSA 키
modulus:
00:cb:35:d6:f0:e2:77:41:4b:ea:39:ea:06:bc:5d:
...
# ===== Kubernetes TLS Secret 생성 =====
# Mkcert created a key (_wildcard.cilium.rocks-key.pem) and a certificate (_wildcard.cilium.rocks.pem) that we will use for the Gateway service.
# Create a Kubernetes TLS secret with this key and certificate:
kubectl create secret tls demo-cert --key=_wildcard.cilium.rocks-key.pem --cert=_wildcard.cilium.rocks.pem # TLS Secret 생성
kubectl get secret demo-cert -o json | jq # 생성된 Secret 확인
# ===== TLS Ingress 리소스 생성 =====
# 6. TLS가 활성화된 Ingress 리소스 생성
cat << EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: tls-ingress
namespace: default
spec:
ingressClassName: cilium # Cilium Ingress Controller 사용
rules:
- host: webpod.cilium.rocks # 첫 번째 호스트 규칙
http:
paths:
- backend:
service:
name: webpod # webpod 서비스로 라우팅
port:
number: 80
path: /
pathType: Prefix
- host: bookinfo.cilium.rocks # 두 번째 호스트 규칙
http:
paths:
- backend:
service:
name: details # /details 경로는 details 서비스로
port:
number: 9080
path: /details
pathType: Prefix
- backend:
service:
name: productpage # 루트 경로는 productpage 서비스로
port:
number: 9080
path: /
pathType: Prefix
tls: # TLS 설정 섹션
- hosts:
- webpod.cilium.rocks
- bookinfo.cilium.rocks
secretName: demo-cert # 위에서 생성한 TLS Secret 참조
EOF
# 7. Ingress 상태 확인 (로드밸런서 IP 할당 확인)
kubectl get ingress tls-ingress
NAME CLASS HOSTS ADDRESS PORTS AGE
tls-ingress cilium webpod.cilium.rocks,bookinfo.cilium.rocks 192.168.10.211 80, 443 8s
# 시스템(OS) 신뢰 저장소에 CA 정보 확인
cat /etc/ssl/certs/ca-certificates.crt
ls -al /etc/ssl/certs/ca-certificates.crt
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 220952 Aug 17 12:20 /etc/ssl/certs/ca-certificates.crt
# Install the Mkcert CA into your system so cURL can trust it:
# mkcert -install은 “내 로컬에서 만든 인증서를 시스템이 믿도록” 환경을 꾸며주는 명령.
mkcert -install
# ===== mkcert CA 설치 과정 상세 설명 =====
1. 로컬 CA(자체 루트 인증기관) 생성
# 아직 없으면 로컬 CA 인증서와 개인키를 만듭니다.
# 파일은 $(mkcert -CAROOT)가 가리키는 사용자 데이터 디렉터리에 저장돼요(예: rootCA.pem, rootCA-key.pem). 이 위치는 mkcert -CAROOT로 확인합니다.
## CA 저장 위치 확인
mkcert -CAROOT # CA 인증서 저장 디렉토리 확인
/root/.local/share/mkcert
ls "$(mkcert -CAROOT)" # CA 파일들 확인
rootCA-key.pem rootCA.pem # 루트 CA 개인키와 인증서
2. 시스템(OS) 신뢰 저장소에 CA를 등록
# 배포판에 맞는 도구(예: Debian/Ubuntu의 update-ca-certificates, RHEL/Fedora의 update-ca-trust, Arch의 trust)를 사용해 루트 CA 인증서를 시스템 신뢰 저장소에 넣습니다.
# 이렇게 하면 OpenSSL/GnuTLS를 쓰는 대부분의 CLI가 이 CA로 서명된 서버 인증서를 신뢰합니다. (curl도 포함)
ls -al /etc/ssl/certs/ca-certificates.crt # 시스템 CA 번들 파일 확인
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 220948 Aug 16 01:04 /etc/ssl/certs/ca-certificates.crt
## 맨 하단에 인증서만 파일로 만들어서 디코딩!
tail -n 50 /etc/ssl/certs/ca-certificates.crt # CA 번들 파일 끝부분 확인
vi 1.pem # 새로 추가된 CA 인증서를 별도 파일로 저장
openssl x509 -in 1.pem -text -noout # 추가된 CA 인증서 상세 정보 확인
Issuer: O = mkcert development CA, OU = root@k8s-ctr, CN = mkcert root@k8s-ctr
Validity
Not Before: Aug 17 03:09:12 2025 GMT
Not After : Aug 17 03:09:12 2035 GMT
Subject: O = mkcert development CA, OU = root@k8s-ctr, CN = mkcert root@k8s-ctr
...
X509v3 extensions:
X509v3 Key Usage: critical
Certificate Sign # 인증서 서명 권한
X509v3 Basic Constraints: critical
CA:TRUE, pathlen:0 # CA 인증서임을 명시
3. NSS(브라우저) 신뢰 저장소에 등록
# Linux에서는 Firefox/Chromium이 쓰는 NSS 데이터베이스에도 CA를 넣습니다(사전에 certutil 설치 필요). Firefox는 브라우저 재시작이 필요합니다
# ===== HTTPS 연결 테스트 =====
# Now let's make a request to the Gateway:
# The data should be properly retrieved, using HTTPS (and thus, the TLS handshake was properly achieved).
# In the next challenge, we will see how to use Gateway API for general TLS traffic.
kubectl get ingress tls-ingress -o jsonpath='{.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].ip}' # 로드밸런서 IP 추출
LBIP=$(kubectl get ingress tls-ingress -o jsonpath='{.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].ip}') # IP를 변수에 저장
# 8. HTTPS로 bookinfo 서비스 테스트 (JSON 응답 확인)
curl -s --resolve bookinfo.cilium.rocks:443:${LBIP} https://bookinfo.cilium.rocks/details/1 | jq
# 9. HTTPS로 webpod 서비스 테스트 (상세 연결 정보 확인)
curl -s --resolve webpod.cilium.rocks:443:${LBIP} https://webpod.cilium.rocks/ -v
...
* CAfile: /etc/ssl/certs/ca-certificates.crt # 시스템 CA 번들 사용
* CApath: /etc/ssl/certs
...
* Server certificate: # 서버 인증서 정보
* subject: O=mkcert development certificate; OU=root@k8s-ctr
* start date: Aug 17 03:11:30 2025 GMT
* expire date: Nov 17 03:11:30 2027 GMT
* subjectAltName: host "webpod.cilium.rocks" matched cert's "*.cilium.rocks" # 도메인 매칭 확인
* issuer: O=mkcert development CA; OU=root@k8s-ctr; CN=mkcert root@k8s-ctr # 발급자 확인
...
Hostname: webpod-697b545f57-nvf6n # 실제 파드 호스트명
IP: 127.0.0.1
IP: ::1
IP: 172.20.0.208 # 파드 IP
IP: fe80::58b2:8ff:fe48:6959
RemoteAddr: 10.0.2.15:34726 # 클라이언트 IP
GET / HTTP/1.1
Host: webpod.cilium.rocks
User-Agent: curl/8.5.0
Accept: */*
X-Envoy-Internal: true # Envoy 프록시 헤더
X-Forwarded-For: 10.0.2.15 # 원본 클라이언트 IP
X-Forwarded-Proto: https # 원본 프로토콜
X-Request-Id: 11e3e44c-f1aa-4939-bec9-06cabb7c76b3 # 요청 ID
✅ 실행 결과 요약
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# mkcert '*.cilium.rocks'
Created a new local CA 💥
Note: the local CA is not installed in the system trust store.
Run "mkcert -install" for certificates to be trusted automatically ⚠️
Created a new certificate valid for the following names 📜
- "*.cilium.rocks"
Reminder: X.509 wildcards only go one level deep, so this won't match a.b.cilium.rocks ℹ️
The certificate is at "./_wildcard.cilium.rocks.pem" and the key at "./_wildcard.cilium.rocks-key.pem" ✅
It will expire on 21 November 2027 🗓
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# ls -l *.pem
-rw------- 1 root root 1704 Aug 21 23:45 _wildcard.cilium.rocks-key.pem
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1452 Aug 21 23:45 _wildcard.cilium.rocks.pem
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# openssl x509 -in _wildcard.cilium.rocks.pem -text -noout
Certificate:
Data:
Version: 3 (0x2)
Serial Number:
aa:04:29:06:5d:e9:96:90:5f:7c:0c:bb:66:c1:b0:2b
Signature Algorithm: sha256WithRSAEncryption
Issuer: O = mkcert development CA, OU = root@k8s-ctr, CN = mkcert root@k8s-ctr
Validity
Not Before: Aug 21 14:45:50 2025 GMT
Not After : Nov 21 14:45:50 2027 GMT
Subject: O = mkcert development certificate, OU = root@k8s-ctr
Subject Public Key Info:
Public Key Algorithm: rsaEncryption
...
X509v3 extensions:
X509v3 Key Usage: critical
Digital Signature, Key Encipherment
X509v3 Extended Key Usage:
TLS Web Server Authentication
X509v3 Authority Key Identifier:
1C:1F:C2:B2:7D:96:F2:D8:6D:F4:D8:53:70:78:F1:BD:FA:55:1F:66
X509v3 Subject Alternative Name:
DNS:*.cilium.rocks
Signature Algorithm: sha256WithRSAEncryption
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# kubectl get ingress tls-ingress
NAME CLASS HOSTS ADDRESS PORTS AGE
tls-ingress cilium webpod.cilium.rocks,bookinfo.cilium.rocks 192.168.10.211 80, 443 5s
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# ls -al /etc/ssl/certs/ca-certificates.crt
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 219342 Feb 17 2025 /etc/ssl/certs/ca-certificates.crt
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# ls -al /etc/ssl/certs/ca-certificates.crt
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 219342 Feb 17 2025 /etc/ssl/certs/ca-certificates.crt
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# mkcert -install
The local CA is now installed in the system trust store! ⚡️
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# mkcert -CAROOT
/root/.local/share/mkcert
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# ls -al /etc/ssl/certs/ca-certificates.crt
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 219342 Feb 17 2025 /etc/ssl/certs/ca-certificates.crt
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# mkcert -install
The local CA is now installed in the system trust store! ⚡️
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# mkcert -CAROOT
/root/.local/share/mkcert
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# kubectl get ingress tls-ingress -o jsonpath='{.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].ip}'
192.168.10.211(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# LBIP=$(kubectl get ingress tls-ingress -o jsonpath='{.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].ip}')
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# curl -s --resolve bookinfo.cilium.rocks:443:${LBIP} https://bookinfo.cilium.rocks/details/1 | jq
{
"id": 1,
"author": "William Shakespeare",
"year": 1595,
"type": "paperback",
"pages": 200,
"publisher": "PublisherA",
"language": "English",
"ISBN-10": "1234567890",
"ISBN-13": "123-1234567890"
}
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# curl -s --resolve webpod.cilium.rocks:443:${LBIP} https://webpod.cilium.rocks/ -v
* Added webpod.cilium.rocks:443:192.168.10.211 to DNS cache
* Hostname webpod.cilium.rocks was found in DNS cache
* Trying 192.168.10.211:443...
* Connected to webpod.cilium.rocks (192.168.10.211) port 443
* ALPN: curl offers h2,http/1.1
...
X-Envoy-Internal: true
X-Forwarded-For: 10.0.2.15
X-Forwarded-Proto: https
X-Request-Id: e1736d01-c3d8-4920-a6fe-7fcfff21960b
* Connection #0 to host webpod.cilium.rocks left intact
Gateway API Support
Gateway API는 Ingress를 대체하는 리소스입니다.
Gateway API의 주요 특징을 정리하면 다음과 같습니다.
- 세분화된 리소스 모델: GatewayClass, Gateway, Route(HTTPRoute, TCPRoute 등)와 같은 리소스를 통해 라우팅 규칙을 더 세밀하게 정의할 수 있습니다.
- 프로토콜 독립성: HTTP뿐만 아니라 TCP, UDP, TLS 등 다양한 프로토콜을 지원합니다.
- 보안 강화: TLS 구성과 세부적인 액세스 제어를 기본적으로 지원합니다.
- 교차 네임스페이스 라우팅: 서로 다른 네임스페이스의 서비스로 트래픽을 라우팅할 수 있어 아키텍처의 유연성이 높아집니다.
- 확장성: 사용자 정의 리소스와 정책을 통해 손쉽게 확장할 수 있습니다.
- 역할 기반 설계: 클러스터 운영자, 개발자, 보안 담당자 등 역할별로 리소스와 책임을 분리할 수 있습니다.
아래 그림은 Kubernetes Gateway API의 리소스 구조와 트래픽 흐름을 시각화한 것입니다.

- GatewayClass: 클러스터 관리자가 정의하는 인프라(LoadBalancer, 클라우드 등) 유형을 나타냅니다.
- Gateway: 실제로 외부 트래픽을 수신하는 진입점(LoadBalancer, IP, 포트 등)을 정의하며, GatewayClass를 참조합니다.
- Route(HTTPRoute 등): 개발자가 서비스별로 작성하는 라우팅 규칙으로, Gateway에 연결되어 트래픽을 특정 서비스로 전달합니다.
- 트래픽 흐름:
- 외부 사용자의 요청이 Gateway(LoadBalancer, NodePort 등)로 들어옵니다.
- Gateway는 연결된 Route(HTTPRoute, TCPRoute 등)의 규칙에 따라 트래픽을 분기합니다.
- Route는 트래픽을 클러스터 내부의 Service로 전달합니다.
- 교차 네임스페이스: Route와 Service가 서로 다른 네임스페이스에 존재할 수 있어, 유연한 서비스 연결이 가능합니다.
이 구조는 역할 분리(운영자/개발자), 다양한 프로토콜 지원, 보안 및 확장성을 강화합니다.](images/6주차/Gateway.webp)
Gateway API 사전 준비
# CRD 설치
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes-sigs/gateway-api/v1.2.0/config/crd/standard/gateway.networking.k8s.io_gatewayclasses.yaml
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes-sigs/gateway-api/v1.2.0/config/crd/standard/gateway.networking.k8s.io_gateways.yaml
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes-sigs/gateway-api/v1.2.0/config/crd/standard/gateway.networking.k8s.io_httproutes.yaml
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes-sigs/gateway-api/v1.2.0/config/crd/standard/gateway.networking.k8s.io_referencegrants.yaml
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes-sigs/gateway-api/v1.2.0/config/crd/standard/gateway.networking.k8s.io_grpcroutes.yaml
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes-sigs/gateway-api/v1.2.0/config/crd/experimental/gateway.networking.k8s.io_tlsroutes.yaml
# 확인
kubectl get crd | grep gateway.networking.k8s.io
gatewayclasses.gateway.networking.k8s.io 2025-08-21T15:14:58Z
gateways.gateway.networking.k8s.io 2025-08-21T15:15:04Z
grpcroutes.gateway.networking.k8s.io 2025-08-21T15:15:17Z
httproutes.gateway.networking.k8s.io 2025-08-21T15:15:08Z
referencegrants.gateway.networking.k8s.io 2025-08-21T15:15:12Z
tlsroutes.gateway.networking.k8s.io 2025-08-21T15:15:21ZCilium Gateway API 설정
helm upgrade cilium cilium/cilium --version 1.18.1 --namespace kube-system --reuse-values \
--set ingressController.enabled=false --set gatewayAPI.enabled=true # Cilium Ingress와 Cilium Gateway API를 동시에 활성화할 수 없으므로 Ingress 비활성화, Gateway API 활성화
kubectl -n kube-system rollout restart deployment/cilium-operator # cilium-operator 디플로이먼트 롤링 재시작
kubectl -n kube-system rollout restart ds/cilium # cilium 데몬셋 롤링 재시작
cilium config view | grep gateway-api # gateway-api 관련 설정 확인
kubectl get svc,pod -n kube-system # kube-system 네임스페이스의 서비스, 파드 상태 확인
kubectl get GatewayClass # GatewayClass 리소스 목록 확인 (cilium-ingress 제거 여부 확인)
kubectl get gateway -A # 모든 네임스페이스의 Gateway 리소스 확인
✅ 실행 결과 요약
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# cilium config view | grep gateway-api
enable-gateway-api true
enable-gateway-api-alpn false
enable-gateway-api-app-protocol false
enable-gateway-api-proxy-protocol false
enable-gateway-api-secrets-sync true
gateway-api-hostnetwork-enabled false
gateway-api-hostnetwork-nodelabelselector
gateway-api-secrets-namespace cilium-secrets
gateway-api-service-externaltrafficpolicy Cluster
gateway-api-xff-num-trusted-hops 0
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# kubectl get svc,pod -n kube-system
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/cilium-envoy ClusterIP None <none> 9964/TCP 2d1h
service/hubble-metrics ClusterIP None <none> 9965/TCP 2d1h
service/hubble-peer ClusterIP 10.96.249.69 <none> 443/TCP 2d1h
service/hubble-relay ClusterIP 10.96.121.75 <none> 80/TCP 2d1h
service/hubble-ui NodePort 10.96.163.103 <none> 80:30003/TCP 2d1h
service/kube-dns ClusterIP 10.96.0.10 <none> 53/UDP,53/TCP,9153/TCP 2d1h
service/metrics-server ClusterIP 10.96.221.127 <none> 443/TCP 2d1h
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/cilium-8hw5c 0/1 Running 0 11s
pod/cilium-envoy-4w8vp 1/1 Running 0 2d1h
pod/cilium-envoy-kfp2b 1/1 Running 0 2d1h
pod/cilium-operator-bfc88c9bf-wkfg8 1/1 Running 0 28s
pod/cilium-twbm4 0/1 Running 0 11s
pod/coredns-674b8bbfcf-29p59 1/1 Running 0 2d1h
pod/coredns-674b8bbfcf-xwh6q 1/1 Running 0 2d1h
pod/etcd-k8s-ctr 1/1 Running 0 2d1h
pod/hubble-relay-fdd49b976-4zrwp 1/1 Running 0 2d1h
pod/hubble-ui-655f947f96-9kkds 2/2 Running 0 2d1h
pod/kube-apiserver-k8s-ctr 1/1 Running 0 2d1h
pod/kube-controller-manager-k8s-ctr 1/1 Running 0 2d1h
pod/kube-scheduler-k8s-ctr 1/1 Running 0 2d1h
pod/metrics-server-5dd7b49d79-mdcnc 1/1 Running 0 2d1h
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# kubectl get GatewayClass
NAME CONTROLLER ACCEPTED AGE
cilium io.cilium/gateway-controller True 4m42s
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# kubectl get gateway
No resources found in default namespace.
기본 동작 원리: 개요 - Docs
- Cilium 배포에는 Gateway API 리소스를 처리하는 두 가지 구성 요소가 있습니다: Cilium 에이전트와 Cilium 오퍼레이터입니다.
- Cilium 오퍼레이터는 모든 Gateway API 리소스를 감시(watch)하고, 해당 리소스가 유효한지 검증합니다. 리소스가 유효하면 오퍼레이터가 이를 승인(accepted) 상태로 표시합니다. 이 과정이 Cilium Envoy 구성 리소스로 변환되는 절차의 시작입니다.
- 이후 Cilium 에이전트가 Cilium Envoy 구성 리소스를 가져옵니다.
- Cilium 에이전트는 이 리소스를 사용하여 내장된 Envoy 또는 Envoy DaemonSet에 구성을 전달합니다. Envoy가 실제 트래픽 처리를 담당합니다.
Cilium Gateway 배포
#
cat << EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: my-gateway
spec:
gatewayClassName: cilium
listeners:
- protocol: HTTP
port: 80
name: web-gw
allowedRoutes:
namespaces:
from: Same
---
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: HTTPRoute
metadata:
name: http-app-1
spec:
parentRefs:
- name: my-gateway
namespace: default
rules:
- matches:
- path:
type: PathPrefix
value: /details
backendRefs:
- name: details
port: 9080
- matches:
- headers:
- type: Exact
name: magic
value: foo
queryParams:
- type: Exact
name: great
value: example
path:
type: PathPrefix
value: /
method: GET
backendRefs:
- name: productpage
port: 9080
EOF
# You will see a LoadBalancer service named cilium-gateway-my-gateway which was created for the Gateway API.
kubectl get svc,ep cilium-gateway-my-gateway
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/cilium-gateway-my-gateway LoadBalancer 10.96.240.104 192.168.10.211 80:31017/TCP 96s
NAME ENDPOINTS AGE
endpoints/cilium-gateway-my-gateway 192.192.192.192:9999 96s
# 동일한 EXTERNAL-IP가 Gateway에도 할당되어 있음을 확인
kubectl get gateway
NAME CLASS ADDRESS PROGRAMMED AGE
my-gateway cilium 192.168.10.211 True 14s
## Accepted: Gateway 설정이 승인됨
## Programmed: Gateway 설정이 Envoy에 적용됨
## ResolvedRefs: 참조된 secret이 모두 존재하고 권한이 있음
kc describe gateway # Gateway 리소스 상세 정보 확인
#
kubectl get httproutes -A # 모든 네임스페이스의 HTTPRoute 리소스 확인
NAMESPACE NAME HOSTNAMES AGE
default http-app-1 8m12s
# Accepted: HTTPRoute 설정이 올바르고 승인됨
# ResolvedRefs: 참조된 서비스가 모두 존재하고 유효함
kc describe httproutes # HTTPRoute 리소스 상세 정보 확인
# Cilium Operator 로그에서 gateway 관련 이벤트 확인
kubectl logs -n kube-system deployments/cilium-operator | grep gateway✅ 실행 결과 요약
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# kubectl get svc,ep cilium-gateway-my-gateway
Warning: v1 Endpoints is deprecated in v1.33+; use discovery.k8s.io/v1 EndpointSlice
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/cilium-gateway-my-gateway LoadBalancer 10.96.214.33 192.168.10.211 80:31152/TCP 10s
NAME ENDPOINTS AGE
endpoints/cilium-gateway-my-gateway 192.192.192.192:9999 10s
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# kubectl get gateway
NAME CLASS ADDRESS PROGRAMMED AGE
my-gateway cilium 192.168.10.211 True 14s
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# kc describe gateway
Name: my-gateway
Namespace: default
...
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# kubectl get httproutes -A
NAMESPACE NAME HOSTNAMES AGE
default http-app-1 22s
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# kc describe httproutes
...
Rules:
Backend Refs:
Group:
Kind: Service
Name: details
Port: 9080
Weight: 1
Matches:
Path:
Type: PathPrefix
Value: /details
Backend Refs:
Group:
Kind: Service
Name: productpage
Port: 9080
Weight: 1
Matches:
Headers:
Name: magic
Type: Exact
Value: foo
Method: GET
Path:
Type: PathPrefix
Value: /
Query Params:
Name: great
Type: Exact
Value: example
...
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# kubectl logs -n kube-system deployments/cilium-operator | grep gateway
time=2025-08-21T15:22:50.933923572Z level=info msg=" --egress-gateway-reconciliation-trigger-interval='1s'" subsys=cilium-operator-generic
time=2025-08-21T15:22:50.933997447Z level=info msg=" --enable-egress-gateway='false'" subsys=cilium-operator-generic
...요청 보내기
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# GATEWAY=$(kubectl get gateway my-gateway -o jsonpath='{.status.addresses[0].value}')
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# echo $GATEWAY
192.168.10.211
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# curl --fail -s http://"$GATEWAY"/details/1 | jq
{
"id": 1,
"author": "William Shakespeare",
"year": 1595,
"type": "paperback",
"pages": 200,
"publisher": "PublisherA",
"language": "English",
"ISBN-10": "1234567890",
"ISBN-13": "123-1234567890"
}
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# curl -v -H 'magic: foo' http://"$GATEWAY"\?great\=example
* Trying 192.168.10.211:80...
* Connected to 192.168.10.211 (192.168.10.211) port 80
> GET /?great=example HTTP/1.1
> Host: 192.168.10.211
...HTTPS Example
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# cat << EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: tls-gateway
spec:
gatewayClassName: cilium
listeners:
- name: https-1
protocol: HTTPS
port: 443
hostname: "bookinfo.cilium.rocks"
tls:
certificateRefs:
- kind: Secret
name: demo-cert
- name: https-2
protocol: HTTPS
port: 443
hostname: "webpod.cilium.rocks"
tls:
certificateRefs:
- kind: Secret
name: demo-cert
---
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: HTTPRoute
metadata:
name: https-app-route-1
spec:
parentRefs:
- name: tls-gateway
hostnames:
- "bookinfo.cilium.rocks"
EOF port: 80bpodPrefix"rking.k8s.io/v1
gateway.gateway.networking.k8s.io/tls-gateway created
httproute.gateway.networking.k8s.io/https-app-route-1 created
httproute.gateway.networking.k8s.io/https-app-route-2 created
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# kubectl get gateway tls-gateway
NAME CLASS ADDRESS PROGRAMMED AGE
tls-gateway cilium 192.168.10.213 True 5s
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# kubectl get httproutes https-app-route-1 https-app-route-2
NAME HOSTNAMES AGE
https-app-route-1 ["bookinfo.cilium.rocks"] 11s
https-app-route-2 ["webpod.cilium.rocks"] 11s
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# GATEWAY2=$(kubectl get gateway tls-gateway -o jsonpath='{.status.addresses[0].value}')
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# echo $GATEWAY2
192.168.10.213
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# curl -s --resolve bookinfo.cilium.rocks:443:${GATEWAY2} https://bookinfo.cilium.rocks/details/1 | jq
{
"id": 1,
"author": "William Shakespeare",
"year": 1595,
"type": "paperback",
"pages": 200,
"publisher": "PublisherA",
"language": "English",
"ISBN-10": "1234567890",
"ISBN-13": "123-1234567890"
}
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# curl -s --resolve webpod.cilium.rocks:443:${GATEWAY2} https://webpod.cilium.rocks/ -v
* Added webpod.cilium.rocks:443:192.168.10.213 to DNS cache
* Hostname webpod.cilium.rocks was found in DNS cache
* Trying 192.168.10.213:443...TLS Route
- Gateway 리소스는 TLS 연결을 종료하고, HTTPRoute로 트래픽을 전달합니다.
- 클라이언트는 HTTPS로 Gateway에 연결합니다.
- Gateway는 TLS 인증서를 사용하여 암호화된 연결을 처리합니다.
- 암호화가 해제된 트래픽은 HTTPRoute에 따라 백엔드 서비스로 전달됩니다.
- HTTPRoute는 호스트명 및 경로에 따라 트래픽을 라우팅합니다.
Terminate 모드(TLS 종료):
- 클라이언트는 Gateway에 HTTPS(암호화된)로 접속합니다.
- Gateway는 TLS 인증서를 사용해 클라이언트와의 암호화된 연결을 종료(TLS Termination)합니다.
- Gateway 내부에서는 암호화가 해제된 HTTP 트래픽으로 백엔드 Pod로 전달합니다.
- 즉, Gateway에서 암호화가 해제되고, 이후 트래픽은 평문 HTTP로 이동합니다.
Passthrough 모드(TLS 패스스루):
- 클라이언트는 Gateway에 HTTPS(암호화된)로 접속합니다.
- Gateway는 TLS 연결을 종료하지 않고, 암호화된 트래픽을 그대로 백엔드 Pod로 전달합니다.
- 백엔드 Pod(서비스)가 직접 TLS 인증서를 가지고 있어, Pod에서 암호화가 해제됩니다.
- 즉, Gateway는 단순히 암호화된 트래픽을 전달만 하고, 실제 TLS 처리는 백엔드에서 수행합니다.
### Deploy Sample App
cat <<'EOF' > nginx.conf
events {
}
http {
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] $status '
'"$request" $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log main;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log;
server {
listen 443 ssl;
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
index index.html;
server_name nginx.cilium.rocks;
ssl_certificate /etc/nginx-server-certs/tls.crt;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/nginx-server-certs/tls.key;
}
}
EOF
# As you can see, it listens on port 443 for SSL traffic. Notice it specifies the certificate and key previously created.
# We will need to mount the files to the right path (/etc/nginx-server-certs) when we deploy the server.
# The NGINX server configuration is held in a Kubernetes ConfigMap. Let's create it.
kubectl create configmap nginx-configmap --from-file=nginx.conf=./nginx.conf
# Review the NGINX server Deployment and the Service fronting it:
cat << EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: my-nginx
labels:
run: my-nginx
spec:
ports:
- port: 443
protocol: TCP
selector:
run: my-nginx
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: my-nginx
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
run: my-nginx
replicas: 1
template:
metadata:
labels:
run: my-nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: my-nginx
image: nginx
ports:
- containerPort: 443
volumeMounts:
- name: nginx-config
mountPath: /etc/nginx
readOnly: true
- name: nginx-server-certs
mountPath: /etc/nginx-server-certs
readOnly: true
volumes:
- name: nginx-config
configMap:
name: nginx-configmap
- name: nginx-server-certs
secret:
secretName: demo-cert
EOF
# Verify the Service and Deployment have been deployed successfully:
kubectl get deployment,svc,ep my-nginx
### Deploy Gateway
cat << EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: cilium-tls-gateway
spec:
gatewayClassName: cilium
listeners:
- name: https
hostname: "nginx.cilium.rocks"
port: 443
protocol: TLS
tls:
mode: Passthrough
allowedRoutes:
namespaces:
from: All
---
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1alpha2
kind: TLSRoute
metadata:
name: nginx
spec:
parentRefs:
- name: cilium-tls-gateway
hostnames:
- "nginx.cilium.rocks"
rules:
- backendRefs:
- name: my-nginx
port: 443
EOF
# The Gateway does not actually inspect the traffic aside from using the SNI header for routing. Indeed the hostnames field defines a set of SNI names that should match against the SNI attribute of TLS ClientHello message in TLS handshake.
# Let's now deploy the Gateway and the TLSRoute to the cluste
kubectl get gateway cilium-tls-gateway
NAME CLASS ADDRESS PROGRAMMED AGE
cilium-tls-gateway cilium 172.18.255.202 True 8s
GATEWAY=$(kubectl get gateway cilium-tls-gateway -o jsonpath='{.status.addresses[0].value}')
echo $GATEWAY
# Let's also double check the TLSRoute has been provisioned successfully and has been attached to the Gateway.
kubectl get tlsroutes.gateway.networking.k8s.io -o json | jq '.items[0].status.parents[0]'
###요청 보내기
curl -v --resolve "nginx.cilium.rocks:443:$GATEWAY" "https://nginx.cilium.rocks:443"
✅ 실행 결과 요약
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# kubectl get deployment,svc,ep my-nginx
\Warning: v1 Endpoints is deprecated in v1.33+; use discovery.k8s.io/v1 EndpointSlice
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment.apps/my-nginx 1/1 1 1 13s
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/my-nginx ClusterIP 10.96.42.246 <none> 443/TCP 13s
NAME ENDPOINTS AGE
endpoints/my-nginx 172.20.1.247:443 13s
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# kubectl get gateway cilium-tls-gateway
NAME CLASS ADDRESS PROGRAMMED AGE
cilium-tls-gateway cilium 192.168.10.214 True 6s
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# GATEWAY=$(kubectl get gateway cilium-tls-gateway -o jsonpath='{.status.addresses[0].value}')
echo $GATEWAY
192.168.10.214
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# curl -v --resolve "nginx.cilium.rocks:443:$GATEWAY" "https://nginx.cilium.rocks:443"
* Added nginx.cilium.rocks:443:192.168.10.214 to DNS cache
* Hostname nginx.cilium.rocks was found in DNS cache
* Trying 192.168.10.214:443...
* Connected to nginx.cilium.rocks (192.168.10.214) port 443
* ALPN: curl offers h2,http/1.1
* TLSv1.3 (OUT), TLS handshake, Client hello (1):
...Gateway의 External IP를 직접 지정하기
# Api GW 스펙 변경
spec:
addresses:
- type: IPAddress
value: 192.168.10.215
gatewayClassName: cilium
...
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# GATEWAY=$(kubectl get gateway cilium-tls-gateway -o jsonpath='{.status.addresses[0].value}')
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# echo $GATEWAY
192.168.10.215
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# curl -v --resolve "nginx.cilium.rocks:443:$GATEWAY" "https://nginx.cilium.rocks:443"
* Added nginx.cilium.rocks:443:192.168.10.215 to DNS cache
* Hostname nginx.cilium.rocks was found in DNS cache
* Trying 192.168.10.215:443...
* Connected to nginx.cilium.rocks (192.168.10.215) port 443
Mutual Authentication(Beta)
Cilium의 Mutual Authentication(mTLS)은 클라이언트와 서버 간의 양방향 인증을 제공하는 고급 보안 기능입니다. 일반적인 TLS에서는 서버만 인증서를 제공하지만, mTLS에서는 클라이언트도 인증서를 제공하여 서로를 신뢰할 수 있는지 확인합니다.
mTLS 개요 및 아키텍처
Cilium은 PIRE(SPIFFE Runtime Environment)와 SPIFFE(SPIFFE Identity Framework)를 활용하여 mTLS를 구현합니다.
mTLS 인증 과정:

- 클라이언트와 서버 워크로드 각각에 SPIRE가 SPIFFE ID와 SVID(인증서)를 발급합니다.
- 클라이언트가 서버에 접속을 시도하면, 양쪽 모두 자신의 인증서를 상대방에게 전달합니다(mTLS 핸드셰이크).
- Cilium Proxy가 클라이언트와 서버가 제출한 인증서를 상호 검증하여, 신뢰할 수 있는지 확인합니다.
- 인증서 검증이 성공하면, 클라이언트와 서버 간에 암호화된 통신이 시작됩니다.
SPIFFE/SPIRE 의 Entity:
- SPIFFE ID: 워크로드의 고유한 신원을 정의 (
spiffe://trust-domain/workload-identifier) - SPIRE Server: 인증서 발급 및 관리 담당
- SPIRE Agent: 워크로드와 직접 상호작용하여 SVID(SPIFFE Verifiable Identity Document) 제공
- Cilium Agent: SPIRE Agent와 통신하여 워크로드에 SVID 제공 및 mTLS 연결 관리
mTLS 인증 과정:
- SPIFFE ID 발급: SPIRE가 클라이언트와 서버 워크로드에 각각 SVID 발급
- mTLS 핸드셰이크: 클라이언트와 서버가 각각의 인증서를 교환
- 인증서 검증: Cilium Proxy가 양방향 인증서 검증 수행
- 암호화된 통신: 검증 완료 후 암호화된 통신 시작
mTLS 보안 정책
1. 네트워크 정책과 mTLS 통합
- CiliumNetworkPolicy에서 인증 모드를 "required"로 설정
- 특정 SPIFFE ID를 가진 클라이언트만 접근 허용
- 신뢰 도메인(trust domain) 기반 인증
2. 서비스 메시 정책
- AuthorizationPolicy를 통한 세밀한 접근 제어
- SPIFFE ID 기반 권한 관리
- HTTP 메서드 및 경로별 접근 제한
mTLS의 장점
클라이언트와 서버가 모두 인증서 기반으로 상호 인증을 수행하여 스푸핑 공격을 방지하고 신원 기반의 접근 제어가 가능하다는 점이 있습니다.
또한, 네트워크 위치와 무관하게 신원 기반 접근 제어가 적용되며, 모든 통신이 암호화되고 지속적으로 인증과 권한 검증이 이루어져 제로 트러스트 보안 모델을 실현할 수 있습니다. SPIRE를 통해 인증서가 자동으로 발급 및 갱신되어 수동 관리가 필요 없고, 인증서의 수명 주기도 자동화됩니다.
마지막으로, SPIFFE ID를 기반으로 세밀한 권한 제어가 가능해 서비스 간 통신을 제한하거나 네임스페이스 및 서비스 계정별로 접근을 제어할 수 있습니다.
Cilium mTLS 전체 동작 과정

SPIRE Server (인증서 발급 기관)
- 클러스터에 배포된 SPIRE Server가 인증서 발급 기관(Certificate Authority) 역할을 수행합니다.
- SPIFFE ID를 기반으로 X.509 인증서나 JWT 토큰 형태의 SVID를 발급합니다.
- 모든 인증서의 신뢰성을 보장하는 루트 인증 기관 역할을 담당합니다.
SPIRE Agent (워크로드 인터페이스)
- 각 노드에 배포되어 워크로드와 직접 상호작용합니다.
- 새로운 Pod가 생성되면 해당 워크로드를 식별하고 SPIFFE ID를 생성합니다.
- SPIRE Server로부터 발급받은 SVID를 워크로드에 제공합니다.
Cilium Agent (네트워크 정책 관리)
- SPIRE Agent와 통신하여 워크로드에 필요한 인증 정보를 받아옵니다.
- 네트워크 정책을 관리하고 mTLS 연결을 설정합니다.
- 워크로드 간 통신을 제어하고 보안 정책을 적용합니다.
mTLS 연결 및 통신 과정
- 클라이언트-서버 연결: 클라이언트 Pod가 서버 Pod에 연결을 시도합니다.
- 양방향 인증서 교환: mTLS 핸드셰이크 과정에서 클라이언트와 서버 모두가 인증서를 제공합니다.
- 인증서 검증: Cilium Agent가 양방향 인증서의 유효성을 검증하고 신뢰 도메인을 확인합니다.
- 암호화된 통신: 인증 성공 후 클라이언트와 서버 간에 암호화된 통신이 시작됩니다.
- 보안 정책 적용: 네트워크 정책과 서비스 메시 정책이 적용되어 세밀한 접근 제어가 이루어집니다.
- 지속적인 모니터링: Hubble과 Prometheus를 통해 mTLS 연결 상태와 성능을 실시간으로 모니터링합니다.
- 자동화된 관리: SPIRE가 인증서의 자동 갱신과 정책 업데이트를 관리합니다.
전체 동작 흐름:
- 초기 설정: SPIRE Server와 Agent가 배포되어 인증서 발급 환경을 구축합니다.
- 워크로드 등록: 새로운 Pod가 생성되면 SPIRE Agent가 식별하고 SPIFFE ID를 생성합니다.
- 인증서 발급: SPIRE Server가 SPIFFE ID를 기반으로 SVID를 발급하고 워크로드에 제공합니다.
- mTLS 통신: 클라이언트와 서버가 양방향 인증을 통해 암호화된 통신을 수행합니다.
- 보안 관리: Cilium Agent가 네트워크 정책을 적용하고 지속적인 모니터링을 수행합니다.
L7-Aware Traffic Management
Cilium의 L7(레이어 7) 인식 트래픽 관리는 애플리케이션 레벨에서 세밀한 제어와 관찰성을 제공하는 핵심 기능입니다. 이를 통해 HTTP 메서드, 경로, 헤더 등 애플리케이션 레벨의 정보를 기반으로 트래픽을 관리할 수 있습니다.
HTTP 트래픽 관찰성 (Observing HTTP Traffic)
L7 Cilium Network Policies의 관찰성 이점:
- L7 Cilium Network Policies를 사용할 때 얻는 가장 큰 이점 중 하나는 향상된 관찰성입니다.
- Envoy를 활용하여 Kubernetes 클러스터 내 Pod 간 HTTP 메서드, 경로, 헤더 등의 L7 가시성을 제공합니다.
- 워크로드를 수정하거나 추가적인 Service Mesh 솔루션을 배포할 필요 없이 L7 가시성을 확보할 수 있습니다.
관찰 가능한 L7 정보:
- HTTP 메서드: GET, POST, PUT, DELETE 등
- HTTP 경로:
/v1/request-landing,/api/users등 - HTTP 헤더: Content-Type, Authorization, User-Agent 등
- 응답 코드: 200, 404, 500 등
- 요청/응답 크기: 바이트 단위 트래픽량
고급 Envoy 사용 사례 (Advanced Envoy Use Cases)
Cilium의 Envoy 활용:
- Cilium은 Ingress 및 Gateway API 지원을 포함한 다양한 기능에 Envoy를 활용합니다.
- Cilium은 Envoy 구성에 대한 추상화를 제공하지만, 모든 가능한 시나리오를 커버하지는 않습니다.
Cilium Envoy Config CRDs:
- 원하는 기능을 구현하기 위해 Envoy를 직접 구성할 수 있는 "Cilium Envoy Config CRDs"를 제공합니다.
- 이를 통해 사용자 정의 Envoy 설정을 적용할 수 있습니다.
- Ingress Controller 및 Gateway API 실습을 통해 고급 기능을 탐색할 수 있습니다.
L7에서 트래픽 보안 (Securing Traffic at L7)
표준 Kubernetes Network Policies vs Cilium L7:
Layer 3 (네트워크 레벨):
- 표준 Kubernetes 정책은 신원(일반적으로 IP 주소)을 기반으로 통신을 허용합니다.
- 사용되는 포트나 교환되는 내용에 관계없이 통신이 허용됩니다.
Layer 4 (전송 레벨):
- 포트 기반 필터링을 추가합니다 (예: TCP/80).
- 여전히 실제 트래픽 내용을 검사하거나 필터링하지 않습니다.
Cilium L7 (애플리케이션 레벨):
- Envoy L7 프록시를 활용하여 보안을 강화합니다.
- Layer 7에서 트래픽을 필터링할 수 있습니다.
- 애플리케이션이 공유하는 정보 유형을 기반으로 필터링할 수 있습니다:
- HTTP 경로
- HTTP 헤더
- 기타 애플리케이션 레벨 속성
Cilium Envoy 프록시 통합 방식의 진화
Embedded Envoy Proxy
- Cilium은 이미 L7 정책 및 관찰성을 위해 특정 프로토콜에 Envoy를 사용하고 있습니다.
- 이 동일한 구성 요소가 많은 인기 있는 서비스 메시 구현에서 사이드카 프록시로 사용됩니다.
- Cilium 서비스 메시는 사이드카 없는(sidecar-less) 구성으로도 Envoy를 활용합니다.
Envoy as a process in the Cilium Agent
- Cilium 1.16 버전까지는 Envoy 프로세스가 각 Cilium 파드 내에서 필요할 때마다 임시(ad-hoc) 방식으로 시작되었습니다.
- L7 네트워크 정책이 워크로드에 적용되어야 할 때 Envoy가 시작됩니다.
- Cilium 에이전트와 Envoy 프록시가 동일한 생명주기를 공유합니다.
A Separate DaemonSet for Envoy
- Cilium 1.14 버전에서 Envoy를 별도의 DaemonSet으로 지원하기 시작했습니다.
- 제공하는 이점들:
- Cilium 에이전트 재시작(예: 업그레이드 목적)이 Envoy를 통해 프록시되는 실시간 트래픽에 영향을 미치지 않습니다.
- Envoy 패치 릴리스 업그레이드가 Cilium 에이전트에 영향을 미치지 않습니다.
- Envoy 애플리케이션 로그가 Cilium 에이전트의 로그와 섞이지 않습니다.
- Envoy 프록시를 위한 전용 헬스 프로브(health probes)를 제공합니다.
L7-Aware Traffic Management 활성화
CiliumEnvoyConfig와 CiliumClusterwideEnvoyConfig는 Cilium에서 Envoy 프록시의 동작을 세밀하게 제어할 수 있도록 해주는 Custom Resource Definition(CRD)입니다.
- CiliumEnvoyConfig: 네임스페이스 단위로 Envoy 구성을 적용할 수 있습니다.
- CiliumClusterwideEnvoyConfig: 클러스터 전체에 걸쳐 Envoy 구성을 적용할 수 있습니다.
주의사항
- CiliumEnvoyConfig(CEC)는 검증이 최소화되어 있어, 여러 CEC가 같은 Envoy 설정을 수정하면 예측 불가능한 결과가 나올 수 있습니다.
- 구성 오류에 대한 피드백이 거의 없으므로, 문제가 생기면 EnvoyConfig 내용을 직접 확인해야 합니다.
- 자동 생성된 구성과 충돌하거나 수정하는 CEC를 만들면 동작이 불안정해질 수 있으니 주의가 필요합니다.
- CEC를 직접 만들 때 E/W 트래픽을 관리하려면 cilium.io/use-original-source-address: "false" 레이블을 꼭 설정해야 하며, 그렇지 않으면 네트워크 충돌이 발생할 수 있습니다.
초기 설정
# Cilium을 Helm으로 업그레이드 및 L7 Envoy 프록시 활성화
helm upgrade cilium cilium/cilium --version 1.18.1 --namespace kube-system --reuse-values \
--set ingressController.enabled=true \ # Ingress Controller 활성화
--set gatewayAPI.enabled=false \ # Gateway API 비활성화
--set envoyConfig.enabled=true \ # EnvoyConfig CRD 활성화
--set loadBalancer.l7.backend=envoy # L7 LoadBalancer 백엔드로 Envoy 사용
# Cilium 구성요소 롤링 재시작 (업그레이드/설정 반영)
kubectl -n kube-system rollout restart deployment/cilium-operator # cilium-operator 재시작
kubectl -n kube-system rollout restart ds/cilium # cilium 데몬셋 재시작
kubectl -n kube-system rollout restart ds/cilium-envoy # cilium-envoy 데몬셋 재시작
# Envoy 관련 설정 및 상태 확인
cilium config view |grep -i envoy # cilium config에서 envoy 관련 설정만 출력
cilium status --wait # cilium 상태가 정상화될 때까지 대기✅ 실행 결과 요약
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# cilium config view |grep -i envoy
enable-envoy-config true
envoy-access-log-buffer-size 4096
envoy-base-id 0
envoy-config-retry-interval 15s
envoy-keep-cap-netbindservice false
envoy-secrets-namespace cilium-secrets
external-envoy-proxy true
loadbalancer-l7 envoy
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# cilium status --wait
/¯¯\
/¯¯\__/¯¯\ Cilium: OK
\__/¯¯\__/ Operator: OK
/¯¯\__/¯¯\ Envoy DaemonSet: OK
\__/¯¯\__/ Hubble Relay: OK
\__/ ClusterMesh: disabled
DaemonSet cilium Desired: 2, Ready: 2/2, Available: 2/2
DaemonSet cilium-envoy Desired: 2, Ready: 2/2, Available: 2/2
Deployment cilium-operator Desired: 1, Ready: 1/1, Available: 1/1
Deployment hubble-relay Desired: 1, Ready: 1/1, Available: 1/1
Deployment hubble-ui Desired: 1, Ready: 1/1, Available: 1/1
Containers: cilium Running: 2
cilium-envoy Running: 2
cilium-operator Running: 1
clustermesh-apiserver
hubble-relay Running: 1
hubble-ui Running: 1
Cluster Pods: 11/11 managed by Cilium
Helm chart version: 1.18.1L7 Load Balancing and URL re-writing
두 개의 백엔드 서비스(echo-service-1과 echo-service-2)에 대한 트래픽을 Envoy를 통해 분산(로드밸런싱)하고, 클라이언트로부터 들어오는 요청의 URL 경로를 지정한 방식으로 변경(URL Re-write)하는 Envoy 리스너를 설정합니다.
- 로드밸런싱:
Envoy는 클라이언트의 요청을 받아 echo-service-1과 echo-service-2로 트래픽을 분산시킵니다. - URL Re-write:
Envoy 리스너의 라우팅 규칙을 통해, 예를 들어/v1/hello로 들어온 요청을 백엔드 서비스에는/hello로 전달하도록 URL 경로를 변경할 수 있습니다. - Envoy 리스너 설정:
이러한 기능을 위해 Envoy의 리스너, 라우트, 클러스터 리소스를 정의하며, 각 리소스는 다음 역할을 합니다.- 리스너(Listener): 외부에서 들어오는 요청을 수신
- 라우트(Route): 요청 경로에 따라 트래픽 분기 및 URL Re-write 규칙 적용
- 클러스터(Cluster): 실제 트래픽이 전달될 백엔드 서비스(echo-service-1, echo-service-2) 정의
# 샘플 애플리케이션 배포
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cilium/cilium/1.18.1/examples/kubernetes/servicemesh/envoy/test-application.yaml
# 확인
## 두 개의 클라이언트 배포 client , client2
## 두 가지 서비스, echo-service-1, echo-service-2
kubectl get -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cilium/cilium/1.18.1/examples/kubernetes/servicemesh/envoy/test-application.yaml
NAME DATA AGE
configmap/coredns-configmap 1 10m
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment.apps/client 1/1 1 1 10m
deployment.apps/client2 1/1 1 1 10m
deployment.apps/echo-service-1 1/1 1 1 10m
deployment.apps/echo-service-2 1/1 1 1 10m
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/echo-service-1 NodePort 10.96.237.117 <none> 8080:31169/TCP 10m
service/echo-service-2 NodePort 10.96.175.3 <none> 8080:32040/TCP 10m
# client2 에 대한 Pod ID로 환경 변수 지정
export CLIENT2=$(kubectl get pods -l name=client2 -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}')
echo $CLIENT2
# Start Observing Traffic with Hubble
cilium hubble port-forward&
hubble observe --from-pod $CLIENT2 -f
# You should be able to get a response from both of the backend services individually from client2:
kubectl exec -it $CLIENT2 -- curl -v echo-service-1:8080/
kubectl exec -it $CLIENT2 -- curl -v echo-service-2:8080/
# Verify that you get a 404 error response if you curl to the non-existent URL /foo on these services:
kubectl exec -it $CLIENT2 -- curl -v echo-service-1:8080/foo
kubectl exec -it $CLIENT2 -- curl -v echo-service-2:8080/foo
< HTTP/1.1 404 Not Found(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# kubectl get -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cilium/cilium/1.18.1/examples/kubernetes/servicemesh/envoy/test-application.yaml
NAME DATA AGE
configmap/coredns-configmap 1 7m18s
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment.apps/client 1/1 1 1 7m18s
deployment.apps/client2 1/1 1 1 7m18s
deployment.apps/echo-service-1 1/1 1 1 7m18s
deployment.apps/echo-service-2 1/1 1 1 7m18s
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/echo-service-1 NodePort 10.96.52.49 <none> 8080:30946/TCP 7m18s
service/echo-service-2 NodePort 10.96.239.85 <none> 8080:31787/TCP 7m18s
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# export CLIENT2=$(kubectl get pods -l name=client2 -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}')
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# echo $CLIENT2
client2-c97ddf6cf-6dln4
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# kubectl exec -it $CLIENT2 -- curl -v echo-service-1:8080/
* Trying 10.96.52.49:8080...
* Connected to echo-service-1 (10.96.52.49) port 8080 (#0)
> GET / HTTP/1.1
> Host: echo-service-1:8080
> User-Agent: curl/7.83.1
> Accept: */*
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# hubble observe --from-pod $CLIENT2 -f
Aug 21 16:53:37.672: default/client2-c97ddf6cf-6dln4 (ID:3787) <> kube-system/kube-dns:53 (world) pre-xlate-fwd TRACED (UDP)
Aug 21 16:53:37.672: default/client2-c97ddf6cf-6dln4 (ID:3787) <> kube-system/coredns-674b8bbfcf-xwh6q:53 (ID:15971) post-xlate-fwd TRANSLATED (UDP)
Aug 21 16:53:37.672: default/client2-c97ddf6cf-6dln4:34116 (ID:3787) -> kube-system/coredns-674b8bbfcf-xwh6q:53 (ID:15971) to-network FORWARDED (UDP)
Aug 21 16:53:37.672: default/client2-c97ddf6cf-6dln4:34116 (ID:3787) -> kube-system/coredns-674b8bbfcf-xwh6q:53 (ID:15971) to-endpoint FORWARDED (UDP)
Aug 21 16:53:37.673: default/client2-c97ddf6cf-6dln4 (ID:3787) <> kube-system/kube-dns:53 (world) pre-xlate-fwd TRACED (UDP)
...
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# hubble observe --from-pod $CLIENT2 -f
Aug 21 16:54:32.160: default/client2-c97ddf6cf-6dln4:51484 (ID:3787) -> kube-system/coredns-674b8bbfcf-xwh6q:53 (ID:15971) to-endpoint FORWARDED (UDP)
Aug 21 16:54:32.160: default/client2-c97ddf6cf-6dln4 (ID:3787) <> kube-system/kube-dns:53 (world) pre-xlate-fwd TRACED (UDP)
Aug 21 16:54:32.160: default/client2-c97ddf6cf-6dln4 (ID:3787) <> kube-system/coredns-674b8bbfcf-xwh6q:53 (ID:15971) post-xlate-fwd TRANSLATED (UDP)
...
L7 정책 추가
# Adding a Layer 7 policy introduces the Envoy proxy into the path for this traffic
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cilium/cilium/1.18.1/examples/kubernetes/servicemesh/envoy/client-egress-l7-http.yaml
# client2 is allowed to contact one.one.one.one/ on port 80 and the echo Pod
# on port 8080. HTTP introspection is enabled for client2.
# The toFQDNs section relies on DNS introspection being performed by
# the client-egress-only-dns policy.
apiVersion: "cilium.io/v2"
kind: CiliumNetworkPolicy
metadata:
name: client-egress-l7-http
spec:
description: "Allow GET one.one.one.one:80/ and GET <echo>:8080/ from client2"
endpointSelector:
matchLabels:
other: client
egress:
# Allow GET / requests towards echo pods.
- toEndpoints:
- matchLabels:
k8s:kind: echo
toPorts:
- ports:
- port: "8080"
protocol: TCP
rules:
http:
- method: "GET"
path: "/"
# Allow GET / requests, only towards one.one.one.one.
- toFQDNs:
- matchName: "one.one.one.one" #허용하는 도메인
toPorts:
- ports:
- port: "80" # 허용하는 포트
protocol: TCP
rules:
http:
- method: "GET"
path: "/"
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cilium/cilium/1.18.1/examples/kubernetes/servicemesh/envoy/client-egress-only-dns.yaml
apiVersion: cilium.io/v2
kind: CiliumNetworkPolicy
metadata:
name: client-egress-only-dns
spec:
endpointSelector:
matchLabels:
kind: client
egress:
- toPorts:
- ports:
- port: "53"
protocol: ANY
rules:
dns:
- matchPattern: "*"
toEndpoints:
- matchLabels:
k8s:io.kubernetes.pod.namespace: kube-system
k8s:k8s-app: kube-dns
- matchLabels:
k8s:io.kubernetes.pod.namespace: kube-system
k8s:k8s-app: coredns
# Make a request to a backend service (either will do):
kubectl exec -it $CLIENT2 -- curl -v echo-service-1:8080/
kubectl exec -it $CLIENT2 -- curl -v echo-service-2:8080/foo
< HTTP/1.1 403 Forbidden
# 레이어 7 정책을 추가하면 레이어 7 가시성이 가능합니다. 이제 허블 출력에 프록시로의 흐름이 포함되어 있으며, 레벨 7에서의 HTTP 프로토콜 정보도 표시됩니다
# 예: HTTP/1.1 GET http://echo-service-1:8080/✅ 실행 결과 요약
# HTTP 정책 추가
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# hubble observe --from-pod $CLIENT2 -f
...
Aug 21 17:16:10.537: default/client2-c97ddf6cf-6dln4:41986 (ID:3787) -> default/echo-service-1-867d69c679-wncb2:8080 (ID:2659) http-request FORWARDED (HTTP/1.1 GET http://echo-service-1:8080/)
Aug 21 17:16:10.554: default/client2-c97ddf6cf-6dln4:41986 (ID:3787) -> default/echo-service-1-867d69c679-wncb2:8080 (ID:2659) to-proxy
...
# /foo 정책 차단됨
ault/echo-service-2-5df858689b-lp7dt:8080 (ID:15710) http-request DROPPED (HTTP/1.1 GET http://echo-service-2:8080/foo)
Aug 21 17:17:02.079: default/client2-c97ddf6cf-6dln4:45198 (ID:37
허블로도 트래픽에 대한 확인이 가능합니다.
Add Envoy load-balancing and URL re-writing
# Envoy 로드 밸런싱 및 URL 재작성 추가 : 두 백엔드 echo-서비스 간에 50/50의 부하 분산 , 경로 /foo를 다시 작성합니다/
# Apply the envoy-traffic-management-test.yaml file, which defines a CiliumClusterwideEnvoyConfig
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cilium/cilium/1.18.1/examples/kubernetes/servicemesh/envoy/envoy-traffic-management-test.yaml
apiVersion: cilium.io/v2
kind: CiliumClusterwideEnvoyConfig
metadata:
name: envoy-lb-listener # Envoy 리스너 리소스 이름
spec:
services:
- name: echo-service-1 # 로드밸런싱 대상 서비스 1
namespace: default
- name: echo-service-2 # 로드밸런싱 대상 서비스 2
namespace: default
resources:
- "@type": type.googleapis.com/envoy.config.listener.v3.Listener
name: envoy-lb-listener # Envoy 리스너 정의
filter_chains:
- filters:
- name: envoy.filters.network.http_connection_manager
typed_config:
"@type": type.googleapis.com/envoy.extensions.filters.network.http_connection_manager.v3.HttpConnectionManager
stat_prefix: envoy-lb-listener
rds:
route_config_name: lb_route # 라우트 설정 이름 지정
use_remote_address: true
skip_xff_append: true
http_filters:
- name: envoy.filters.http.router
typed_config:
"@type": type.googleapis.com/envoy.extensions.filters.http.router.v3.Router
- "@type": type.googleapis.com/envoy.config.route.v3.RouteConfiguration
name: lb_route # 라우트 설정
virtual_hosts:
- name: "lb_route"
domains: [ "*" ] # 모든 도메인 허용
routes:
- match:
prefix: "/" # 모든 경로에 대해 매칭
route:
weighted_clusters:
clusters:
- name: "default/echo-service-1"
weight: 50 # echo-service-1로 50% 트래픽 분산
- name: "default/echo-service-2"
weight: 50 # echo-service-2로 50% 트래픽 분산
retry_policy:
retry_on: 5xx # 5xx 에러 발생 시 재시도
num_retries: 3 # 최대 3회 재시도
per_try_timeout: 1s # 각 시도별 타임아웃 1초
regex_rewrite:
pattern:
google_re2: { }
regex: "^/foo.*$" # /foo로 시작하는 경로를
substitution: "/" # /로 재작성 (URL rewrite)
- "@type": type.googleapis.com/envoy.config.cluster.v3.Cluster
name: "default/echo-service-1"
connect_timeout: 5s # 연결 타임아웃 5초
lb_policy: ROUND_ROBIN # 라운드로빈 방식 로드밸런싱
type: EDS
outlier_detection:
split_external_local_origin_errors: true
consecutive_local_origin_failure: 2 # 2회 연속 실패 시 아웃라이어 처리
- "@type": type.googleapis.com/envoy.config.cluster.v3.Cluster
name: "default/echo-service-2"
connect_timeout: 3s # 연결 타임아웃 3초
lb_policy: ROUND_ROBIN
type: EDS
outlier_detection:
split_external_local_origin_errors: true
consecutive_local_origin_failure: 2
# CiliumClusterwideEnvoyConfig 약자 ccec
kubectl get ccec -o yaml | yq
kubectl get ccec
NAME AGE
envoy-lb-listener 10s
# 50:50 LB 분산 호출됨
kubectl exec -it $CLIENT2 -- curl -v echo-service-1:8080
# A request to /foo should now succeed, because of the path re-writing:
kubectl exec -it $CLIENT2 -- curl -v echo-service-1:8080/foo
# 하지만 네트워크 정책은 여전히 /로 다시 작성되지 않은 경로에 대한 요청을 방지합니다.
# 예를 들어, 이 요청은 패킷이 삭제되고 403 금지 응답 코드가 생성
kubectl exec -it $CLIENT2 -- curl -v echo-service-1:8080/bar
< HTTP/1.1 403 Forbidden
## Output from hubble observe
Aug 17 09:47:32.745: default/client2-c97ddf6cf-8swbm:54094 (ID:16631) -> default/echo-service-1-867d69c679-w4hvn:8080 (ID:2665) http-request DROPPED (HTTP/1.1 GET http://echo-service-1:8080/bar)
# 로그 확인
kubectl -n kube-system logs daemonsets/cilium-envoy
✅ 실행 결과 요약
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# kubectl get ccec
NAME AGE
envoy-lb-listener 23s
#re0writing 동작확인
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# hubble observe --from-pod $CLIENT2 -f
...
Aug 21 17:21:35.761: default/client2-c97ddf6cf-6dln4:60112 (ID:3787) <> 192.168.10.101 (host) pre-xlate-rev TRACED (TCP)
Aug 21 17:21:35.766: default/client2-c97ddf6cf-6dln4:60112 (ID:3787) -> default/echo-service-2-5df858689b-lp7dt:8080 (ID:15710) http-request FORWARDED (HTTP/1.1 GET http://echo-service-1:8080/)
Aug 21 17:21:35.775: default/client2-c97ddf6cf-6dln4:60112 (ID:3787) -> default/echo-service-1:8080 (world) to-proxy FORWARDED (TCP Flags: ACK, FIN)
# 예를 들어, 이 요청은 패킷이 삭제되고 403 금지 응답 코드가 생성
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# kubectl exec -it $CLIENT2 -- curl -v echo-service-1:8080/bar
...
<
Access denied
* Connection #0 to host echo-service-1 left intact
마치며
이번 6주차 실습을 통해 Cilium Service Mesh에 대해 배웠습니다.
특히 Gateway API의 설정과 TLS 인증서 관리, 그리고 mTLS를 통한 양방향 인증 과정을 직접 실습해보면서 Cilium의 고급 네트워킹 기능들을 체험할 수 있었습니다.
Cilium의 Service Mesh 기능과 L7 트래픽 관리, 그리고 Mutual Authentication을 실무에 적용할 때 발생할 수 있는 복잡성과 고려사항들을 스터디를 통해 사전에 파악하여 깊이 있게 고민할 수 있는 귀중한 시간이었습니다.
향후 Cilium 기반 클러스터에서 Gateway API, TLS/mTLS 보안, 그리고 L7 트래픽 관리를 구현할 때 이러한 실습 경험과 지식이 실제 운영에 큰 도움이 될 것으로 기대됩니다.
긴 글 읽어주셔서 감사합니다 :)
'클라우드 컴퓨팅 & NoSQL > [Cilium Study] 실리움 스터디' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [8주차 - Cilium 스터디] Cilium Security & Tetragon (25.08.31) (0) | 2025.09.06 |
|---|---|
| [7주차 - Cilium 스터디] K8S/Cilium Performance (25.08.24) (1) | 2025.08.30 |
| [5주차 - Cilium 스터디] BGP Control Plane & ClusterMesh (25.08.10) (4) | 2025.08.16 |
| [4주차 - Cilium 스터디] Networking - 노드에 파드들간 통신 2 & K8S 외부 노출 (25.08.03) (4) | 2025.08.08 |
| [3주차 - Cilium 스터디] Networking (25.07.27) (0) | 2025.08.02 |
![[6주차 - Cilium 스터디] Cilium ServiceMesh (25.08.17)](https://img1.daumcdn.net/thumb/R750x0/?scode=mtistory2&fname=https%3A%2F%2Fblog.kakaocdn.net%2Fdna%2FysbL8%2FbtsP37Iylp8%2FAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAGxh9jjFib24V0DHyx_nNBGNVRIpYFW5bW5sGEmmngDb%2Fimg.png%3Fcredential%3DyqXZFxpELC7KVnFOS48ylbz2pIh7yKj8%26expires%3D1774969199%26allow_ip%3D%26allow_referer%3D%26signature%3Dv7rWTwuuPRqqF6nP2gE0klDH2AI%253D)